Botrychium jenmanii
Fern Bull. 8: 59. 1900.
Trophophore stalk 2–15 cm, 0.8–1.2 times length of trophophore rachis; blade somewhat dull gray-green, plane, 3-pinnate, to 18 × 26 cm, herbaceous. Pinnae to 5 pairs, well separated, slightly descending to ascending, distance between 1st and 2d pinnae not or slightly more than between 2d and 3d pairs; basal pinnae remotely alternate and long-stalked (basal pinnae in all other botrychiums opposite to subopposite and short-stalked), divided to tip. Pinnules ovate to fan-shaped, margins uniformly denticulate, apex rounded, venation like ribs of fan with short midrib. Sporophores 2-pinnate, 1.2–2.5 times length of trophophore. 2n =180.
Phenology: Leaves green over winter, arising at variable times during last half of summer, meiosis as late as September.
Habitat: Woods and grassy places
Elevation: 50–500 m
Distribution
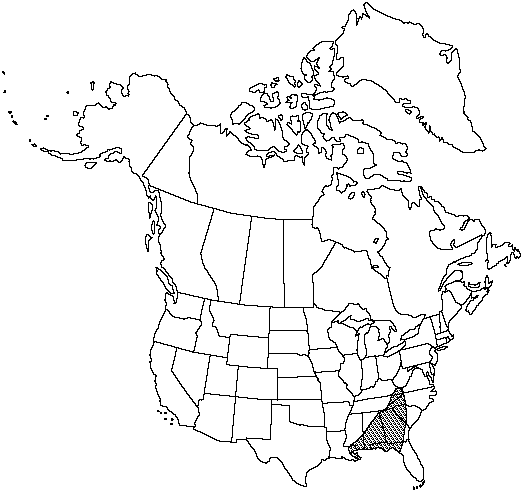
Ala., Fla., Ga., La., Miss., N.C., S.C., Tenn., Va., West Indies in Greater Antilles
Discussion
Botrychium jenmanii occurs in a variety of habitats. In hardwoods and especially pine woods, it is associated with B. biternatum; in open grassy places and lawns it is found with B. lunarioides. In many ways, B. jenmanii is intermediate between B. biternatum and B. lunarioides, and it is possibly their allopolyploid derivative (W. H. Wagner Jr. 1968). It is the only tetraploid among New World members of subg. Sceptidrium.
Selected References
None.