Erigeron maniopotamicus
Sida 21: 673, fig. 1. 2004.
Perennials, 10–22 (–27) cm, taprooted, caudices usually simple, rarely with branches to 20 cm. Stems ascending to decumbent-ascending (usually basally purplish), sparsely to densely strigose (basal-cells inclined, hairs even-width), eglandular. Leaves basal (persistent) and cauline; blades (strongly to weakly 3-nerved) oblanceolate to spatulate-oblanceolate, 30–100 × (3–) 5–12 (–14) mm, cauline gradually reduced distally or not, usually continuing to near heads, margins entire, faces hirsuto-pilose to weakly pilose, eglandular. Heads 1 (–4) (on peduncles 0.5–5 cm), held well beyond leaves at peak flowering, from branches near midstem (or slightly more distal). Involucres (5–) 6–7 × 9–12 (–14) mm. Phyllaries in 2–3 (–4) series, (elliptic to oblong-oblanceolate, abruptly acuminate), hirsuto-strigose to pilose, densely villous at bases, usually eglandular, sometimes sparsely glandular. Ray-florets (16–) 21–33; corollas white to pinkish or purplish, 10–12 mm, laminae not (or weakly) coiling or reflexing. Disc corollas 3.2–3.8 mm. Cypselae 2–2.5 mm, 2-nerved, faces sparsely strigose; pappi: outer of setae, inner of 16–20 bristles.
Phenology: Flowering Jun–Aug.
Habitat: Dry, barren meadows and openings in mixed conifer woodlands
Elevation: 1300–1500 m
Distribution
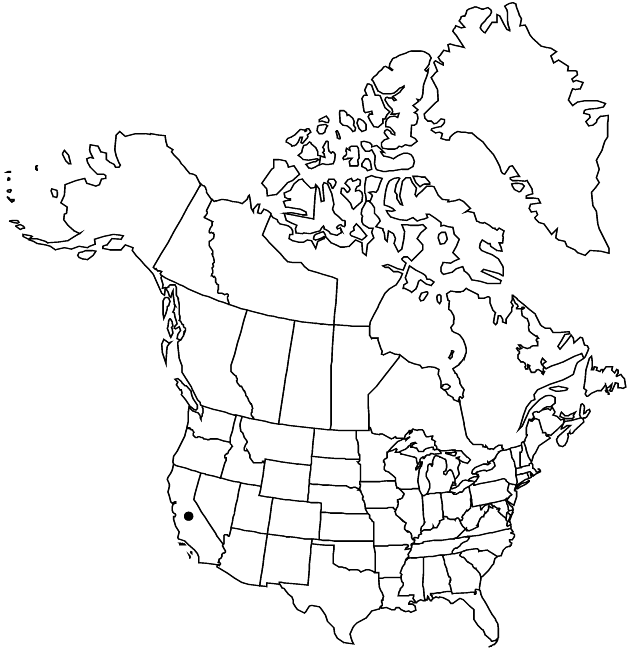
Calif.
Discussion
Of conservation concern.
Selected References
None.