Eupatorium altissimum
Sp. Pl. 2: 837. 1753.
Perennials, 50–150+ cm. Stems (from short caudices or stout rhizomes) single, sparsely branched distally, pubescent throughout (nodes sometimes with galls). Leaves usually opposite (nodes often appearing leafy, lateral buds producing 2+ pairs of leaves); sessile or subsessile; blades strongly 3-nerved from bases, lance-elliptic to oblanceolate, 50–120 × 5–20 mm, bases ± cuneate, margins entire proximally, serrate distally, apices acuminate, faces puberulent or villous, glanddotted. Heads in corymbiform arrays. Phyllaries 8–10 in 2–3 series, oblong, 1–4 × 0.5–1.5 mm, (bases tapered) apices rounded to acute (not mucronate), abaxial faces pubescent throughout. Florets 5; corollas 3–3.5 mm. Cypselae 2–3 mm; pappi of 30–40 bristles 3.5–4 mm. 2n = 20, 30, 40.
Phenology: Flowering Jul–Sep.
Habitat: Clearings, open woods, thickets
Elevation: 20–400 m
Distribution
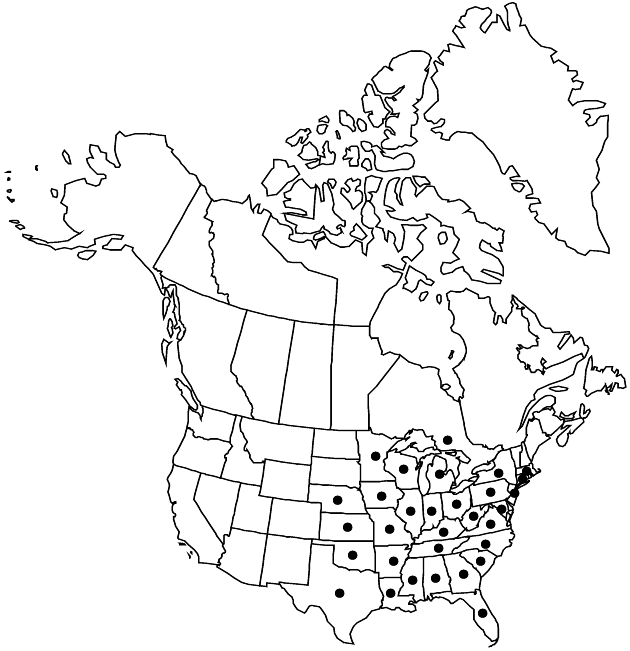
Ont., Ala., Ark., Conn., Fla., Ga., Ill., Ind., Iowa, Kans., Ky., La., Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Miss., Mo., Nebr., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Okla., Pa., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va., W.Va., Wis.
Discussion
Eupatorium altissimum occurs in sexual diploid populations in the Ozark region of Missouri and Arkansas, and as apomictic polyploids elsewhere throughout its range. It occurs almost exclusively on limestone soils, where it is often accompanied by (and sometimes misidentified as) Brickellia eupatorioides, which has 10-ribbed cypselae and plumose pappus bristles. Eupatorium altissimum hybridizes with E. serotinum.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"fine" is not a number.