Nelumbonaceae
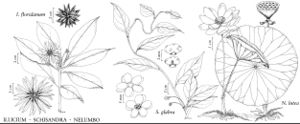
Herbs, perennial, aquatic, rhizomatous; roots adventitious; air chambers conspicuous in vegetative portions of plant. Rhizomes branched, repent, slender, terminal portions becoming tuberous-thickened late in growing season. Leaves arising directly from rhizome, alternate, floating or emersed; petiole long. Leaf-blade peltate, orbiculate, margins entire; laticifers present. Inflorescences axillary, solitary flowers. Flowers bisexual, protogynous, diurnal, borne above water surface; peduncle long; involucre absent; perianth not persistent in fruit (outermost tepals of N. lutea normally persistent), hypogynous; tepals numerous, distinct, outermost reduced, inner tepals becoming larger and more petaloid; stamens numerous; filaments slender; anthers dehiscing by longitudinal slits, connective appendage incurved; pistils numerous, 1-carpellate, separately embedded in flattened top of turbinate receptacle; ovary 1-locular; placentation apical; ovule 1; style short; stigma nearly sessile, capitate. Fruits nutlike, indehiscent, loose in cavities of strongly accrescent receptacle. Seed 1, aril absent; endosperm and perisperm absent; embryo completely filling seed; cotyledons 2, fleshy.
Distribution
Temperate and tropical regions
Discussion
Genus 1, species 2 (2 in the flora).
Nelumbonaceae are pollinated by insects, often by beetles.
Formerly Nelumbonaceae frequently have been included in Nymphaeaceae in the broad sense.
Selected References
None.