Parnassia asarifolia
Jard. Malmaison 1: plate 39. 1804.
Herbs with caudices. Stems 18–50 cm. Leaves: basal in rosettes; petiole 6–17 cm; blade (of larger leaves) reniform to reniform-orbiculate, 20–60 × 25–100 mm, mostly wider than long, base cordate, apex rounded; cauline on proximal 1/2 to middle of stem or absent. Flowers: sepals reflexed in fruit, oblong to obovate, 2.5–6.5 mm, margins hyaline, 0.2–0.4 mm wide, entire, apex rounded; petals 11–18-veined, ovate-elliptic, 10–18 × 7–11 mm, length 2–3 times sepals, base abruptly contracted to 2–3.5 mm claw, margins entire or undulate; stamens 8.5–11.5 mm; anthers 2.2–3.2 mm; staminodes 3-fid almost to base, gland-tipped, 5–9 mm, shorter than stamens, apical glands ovoid-conical, 0.5–0.9 mm; ovary green. Capsules 12 mm. 2n = 32.
Phenology: Flowering summer–early fall.
Habitat: Fens, wet woods, rocky banks, often on acidic soils.
Elevation: 200–1500 m.
Distribution
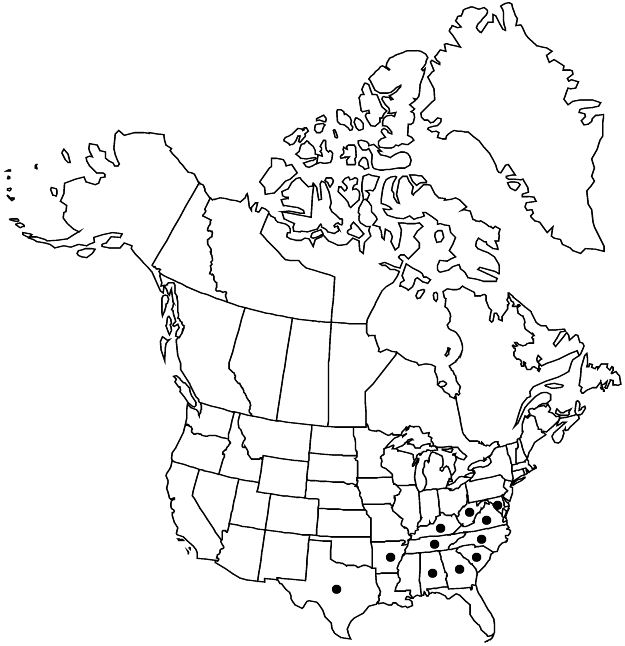
Ala., Ark., Ga., Ky., Md., N.C., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va., W.Va.
Discussion
Parnassia asarifolia is considered endangered in Kentucky and Maryland. It is uncommon throughout its range.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
No values specified.