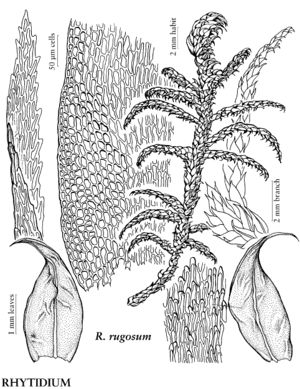
Rhytidium rugosum
Bih. Kongl. Svenska Vetensk.-Akad. Handl. 7(9): 15. 1883.
Plants to 10 cm, yellowish green to golden brown. Stems 2–3 mm wide across leafy stem, turgid from crowded leaves, often hooked at apices, branches to 10 mm. Stem-leaves 2.8–4.5 × 0.8–1.5 mm; alar cells many, 8–20 × 8–12 µm, region broad, triangular, along margin; medial laminal cells 25–55 × 4–6 µm. Branch leaves 1.2–2.3 × 0.4–0.8 mm. Seta 2–2.5 cm. Capsule 2–2.5 mm.
Phenology: Capsules mature summer.
Habitat: Rock, thin layer of soil or humus overlying rock, calcareous or mafic, exposed rock ledges, rocky slopes, bluffs, semi-open dry forests, in tundra, much less common on moist sites
Elevation: low to high elevations (100-3900 m)
Distribution
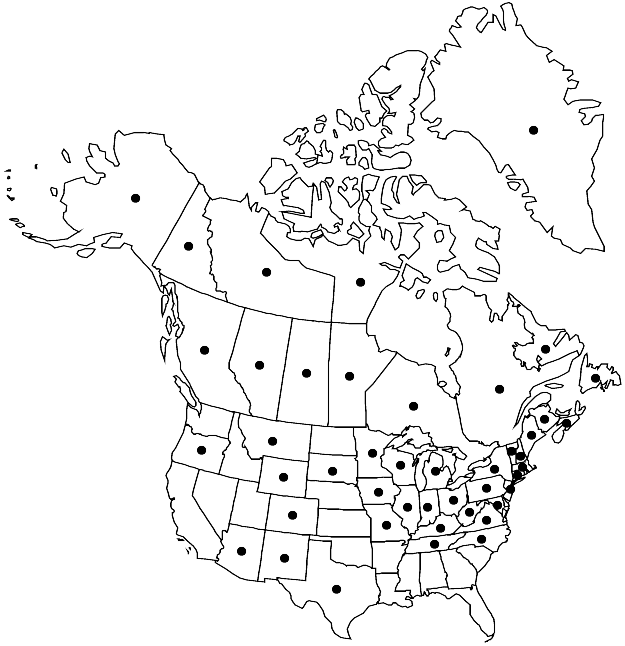
Greenland, Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr., N.W.T., N.S., Nunavut, Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Ariz., Colo., Conn., Ill., Ind., Iowa, Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mo., Mont., N.H., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Oreg., Pa., S.Dak., Tenn., Tex., Vt., Va., W.Va., Wis., Wyo., Mexico, Central America (Guatemala), South America (Bolivia), Eurasia, Africa (Kenya), Africa (Morocco), Africa (Uganda)
Discussion
Though widespread, Rhytidium rugosum is infrequent, presumably because of a preference for exposed calcareous or mafic bedrock in a cool habitat. The plants are rarely found with sporophytes; perhaps almost total reliance on asexual reproduction explains the strong morphological uniformity seen among specimens of R. rugosum collected from across its broad range.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"broad" is not a number.