Sphagnum mirum
Bryologist 106: 501. 2003,.
Plants fairly slender to moderate-sized, green; forming low dense hummocks. Stems yellowish green; 3 layers of superficial cortical cells. Stem-leaves generally longer than branch leaves, 1.1–1.7 mm, lingulate to lingulate-spathulate, hyaline cells mostly nonseptate. Branches terete. Branch fascicles of 2 spreading and 1–2 hanging branches. Branch stems with 1–2 layers of cortical cells. Branch leaves 1–1.4 mm, broadly ovate, with a narrow involute tip; hyaline cells only slightly bulging on either surface, in proximal half of leaf aporose on convex surface and with large faint pores on concave surface; internal commissural walls distinctly papillose; chlorophyllous cells elliptical to elliptical-triangular in transverse-section, enclosed on both surfaces with the widest part in the leaf middle. Sexual condition dioicous. Spores ca. 31 µm, ornamented by small somewhat amalgamated granulae.
Phenology: Sporophytes abundant, capsules mature August.
Habitat: Ecology poorly known but probably quite minerotrophic
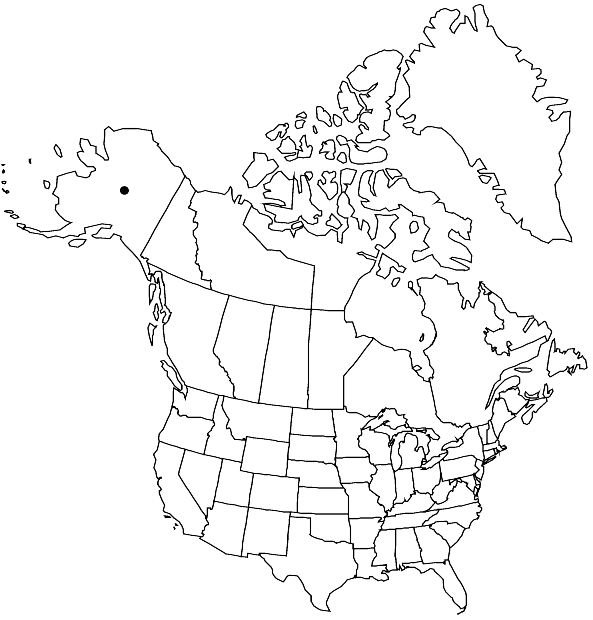
Elevation: low elevations
Discussion
Sphagnum mirum has only been recently discovered and so far is known only from its type locality, where it was growing in a fen mixed with S. teres.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"thinner" is not a number.