Sphagnum obtusum
Bot. Zeitung (Berlin) 35: 478. 1877,.
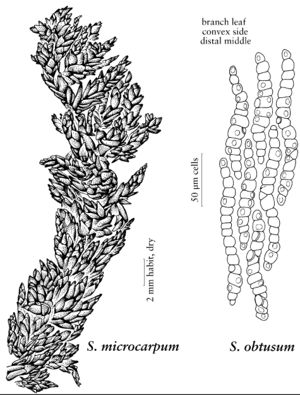
Plants moderate to robust, weak-stemmed, yellow, yellowish-brown to golden brown; capitulum varying from rounded, not 5-radiate and twisted to flat 5-radiate and straight branched. Stem pale green to pale-brown; superficial cortex of weakly to moderately differentiated. Stem-leaves triangular-lingulate, 0.9–1.3 mm; usually appressed; apex obtuse and often erose; hyaline cells efibrillose and nonseptate. Branches tapering or in more robust forms, frequently blunt, straight to arcuate, leaves slightly to moderately elongated at distal end. Branch fascicles with 2 spreading and 2 pendent branches. Branch stems green, with cortex enlarged with conspicuous retort cells. Branch leaves ovate to ovatelanceolate; more than 1.8 mm; straight, stiff, not much undulate and reflexed to recurved; margins entire; hyaline cells on convex surface with a few end pores, but mostly numerous small to very small (often barely visible) pores or wall-thinnings free from the commissures, on concave surface similar, but with pores generally fewer and larger; chlorophyllous cells triangular in transverse-section, just reaching concave surface or slightly enclosed. Sexual condition dioicous. Spores 18–27 µm; both surfaces covered with rough, irregular verrucate plates of papillae, bifurcated Y-mark sculpture on distal surface; proximal laesura less than 0.5 spore radius.
Habitat: Forming carpets in minerotrophic peatlands
Elevation: low to moderate elevations
Distribution
Greenland, Alta., B.C., Man., Nfld. and Labr. (Nfld.), N.W.T., Nunavut, Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Minn., Eurasia
Discussion
Sporophytes are uncommon in Sphagnum obtusum. This is a quite phenotypically variable species that warrants further investigation, which may result in taxonomic splitting. The strongly obtuse stem leaf should separate it from any similar species with which it occurs. Sphagnum mendocinum looks similar phenotypically but there appears to be no range overlap with S. obtusum. The tiny branch leaf pores, which may seem like no more than pinpricks in the cell surface, easily separate S. obtusum microscopically from other species of sect. Cuspidata.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"elongated" is not a number.