Taxiphyllum
Musc. Buitenzorg 4: 1434. 1923.
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
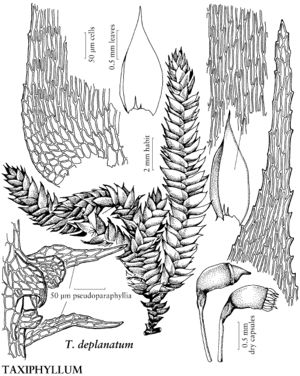 | Taxiphyllum deplanatum | Patricia M. Eckel |
Plants medium-sized to large, in thin to dense mats, light to dark green or yellowish, glossy. Stems creeping, complanate-foliate, sometimes julaceous or subjulaceous, simple or sparingly and irregularly branched, branches not curled when dry; hyalodermis absent, central strand sometimes present; pseudoparaphyllia foliose. Stem and branch leaves similar, erect to widespreading or squarrose, ovate, ovatelanceolate, oblong-lanceolate, or oblong-ovate, widest beyond base, not or occasionally plicate; base not decurrent; margins plane or recurved, serrulate to entire proximally, serrate to serrulate distally; apex acute to subobtuse, sometimes acuminate; costa double and short or sometimes ecostate; alar cells differentiated, quadrate to rectangular; laminal cells smooth or prorulose at distal ends on abaxial surface; basal row of cells smooth; distal cells usually longer than 6: 1. Specialized asexual reproduction absent. Sexual condition dioicous [rarely synoicous], usually sterile; perichaetial leaves ± spreading, lanceolate to ovatelanceolate, apex slenderly acuminate. Seta yellowish to red. Capsule cernuous, oblong-ovoid, straight to arcuate, somewhat contracted below mouth and wrinkled at neck when dry; annulus 2-seriate, persistent; operculum obliquely rostrate; peristome double; exostome teeth cross-striolate proximally, papillose distally; endostome basal membrane high to low, segments keeled, cilia shorter than or same length as segments, in groups of 1–3. Calyptra naked. Spores globose to ovoid, smooth to minutely papillose.
Distribution
North America, Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, terrestrial habitats, primarily on calcareous substrates, temperate, subtropical or tropical regions
Discussion
Species 10–15 (4 in the flora).
Taxiphyllum has stems with small, thick-walled cortical cells, smooth rhizoids in clusters below the leaf insertions usually on the ventral surface of stems, and axillary hairs with one or two, rarely three short basal cells, and one elongate apical cell. The laminal cells are linear-flexuose, or rhomboidal near the apex, and the cell walls are not pitted. The inflorescences occur at the base of stems and branches; the perigonial bracts are small and ovate; the setae are flexuose; the capsules are smooth; and the exostome teeth are bordered and trabeculate.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Stems julaceous to subjulaceous; alar cells 5-12 in marginal row | Taxiphyllum cuspidifolium |
| 1 | Stems complanate-foliate; alar cells 1-8 in marginal row | > 2 |
| 2 | Leaves close, appressed-imbricate, never squarrose; margins plane or rarely recurved basally; alar cells many, in 1-several rows, 3-8 quadrate to short-rectangular cells in marginal row. | Taxiphyllum deplanatum |
| 2 | Leaves usually distant, if imbricate not appressed, often squarrose; margins usually recurved to mid leaf; alar cells few, in 1-3 rows, 1-5 quadrate to short-rectangular cells up margins | > 3 |
| 3 | Leaves ovate to broadly ovate-lanceolate, 0.8-1.6 mm wide; apices often acuminate and twisted; margins plane or rarely recurved; laminal cells smooth. | Taxiphyllum alternans |
| 3 | Leaves ovate, oblong-lanceolate, or rarely narrowly ovate, 0.3-0.6 mm wide; apices acute to acuminate, rarely subobtuse, not twisted; margins narrowly recurved almost to apex; laminal cells smooth or sometimes prorulose at distal ends on abaxial surface. | Taxiphyllum taxirameum |