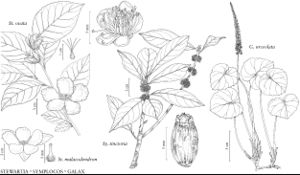
Stewartia ovata
Rhodora 41: 198. 1939 ,.
Shrubs or trees, crown rounded. Stems smooth; young twigs reddish-brown, bark longitudinally fissured. Winter bud-scales 1, enclosed by petiole wings, compressed, 2–5 mm, silvery-pubescent. Leaves: petiole 2–15 mm, wing 1–2 mm wide; blade ovate to widely elliptic, (3–) 8–12 (–15) × (2–) 4–7 (–8.5) cm, base broadly cuneate to rounded, margins serrulate to erose, ciliate, apex acute to acuminate, abaxial surface sparsely pubescent, primary-veins in 5–7 pairs. Inflorescence bracts 1, 10–15 mm. Pedicels 0.3–0.4 (–0.7) cm × 1 mm. Flowers (5–) 6–10 cm diam.; sepals lanceolate, (11–) 14–18 × 6–9 mm; petals 5 (–8), creamy white, margins erose, abaxial surface pubescent; stamens 100–125 (–150); filaments white, yellow, rose, or purple, free portion 12–18 (–20) mm; anthers yellow; styles 5; stigmas unlobed. Capsules ovoid, 1.5–2.2 × 1.4–1.6 cm, apex acute, pubescent. Seeds reddish-brown, winged, planoconvex, (7–) 8–10 × 5–7 mm, dull, wing 0.1–1 mm wide. 2n = 30.
Phenology: Flowering (May-)Jun–Jul(-Oct).
Habitat: Shaded, moist ravines and gorges
Elevation: (100-)200-1100 m
Distribution
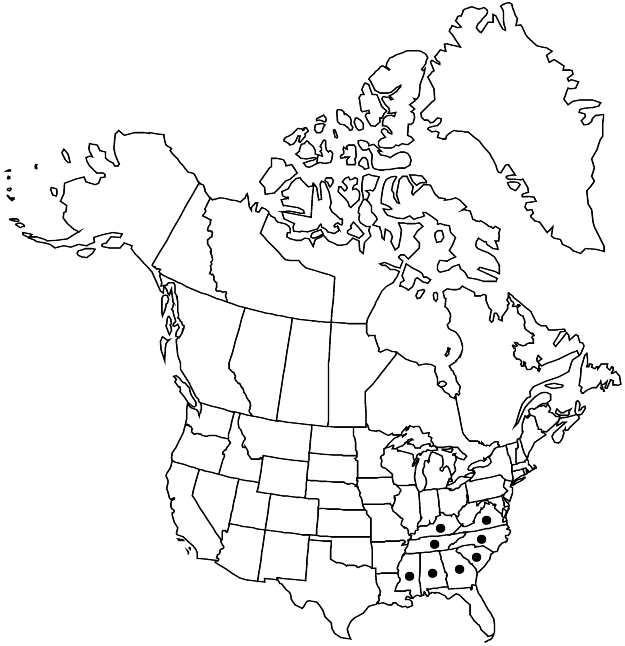
Ala., Ga., Ky., Miss., N.C., S.C., Tenn., Va.
Discussion
Stewartia ovata is likely not naturally occurring in Florida; the only specimen seen is from cultivation in an Alachua County nursery (Wilmot s.n., 21 May 1945, FLAS). Human threats to the species include land-use conversion and habitat fragmentation. A form with purplish filaments [var. grandiflora (Bean) Weatherby] is generally not recognized and is hypothesized to be the result of either genetic instability (C. E. Wood Jr. 1959b) or introgression with S. malacodendron. Stewartia ovata is cultivated as an ornamental for its showy flowers and red fall foliage.
Selected References
None.