familySalviniaceae
genusSalvinia
Show Lower Taxa
Salvinia
Pl. Veron. 3: 52. 1754.
Common names: Floating fern water spangles
Etymology: for Antonia Maria Salvini,1653--1729, an Italian professor of Greek who helped Micheli with his botanical work.
Treatment appears in FNA Volume 2.
Revision as of 14:27, 15 December 2020 by RevisionBot (talk | contribs) (Bot: Adding category Revised Since Print)
| Taxon | Illustrator ⠉ | |
|---|---|---|
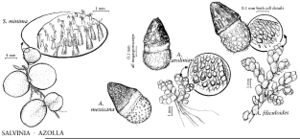 | Azolla filiculoides Azolla mexicana Azolla caroliniana Salvinia minima | John Myers John Myers John Myers John Myers |
Stems with many multicellular hairs. Leaves horizontally spreading. Blades of floating leaves green and pubescent abaxially (on side away from water). Sporocarps borne on chainlike or cymelike organs or submerged leaves; sporangia indehiscent, dispersed as units when sporocarps decay.
Distribution
Mostly tropical, North America, Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America, Eurasia, Africa including Madagascar
Discussion
Leaf development in Salvinia is unique. The upper side of the floating leaf, which appears to face the stem axis, is morphologically abaxial (J. G. Croxdale 1978, 1979, 1981).
Species ca. 10 (1 in the flora).
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
... more about "Salvinia"
directed +
green +
pubescent +
for Antonia Maria Salvini,1653--1729, an Italian professor of Greek who helped Micheli with his botanical work. +
multicellular +
many +
basifixed +
membranous +
entire +
green +
floating +
submerged +
spreading +
downward +
protruding +
single +
protruding +
Pl. Veron. +
1754 +
true +
indehiscent +
dispersed +
trilete +
globose +
branched +
creeping +
water +
Salvinia +
Salviniaceae +
genus +
small +