Solidago simplex
in A. von Humboldt et al., Nov. Gen. Sp. 4(fol.): 81. 1818.
4(qto.): 103. 1820.
Plants 5–80 cm; caudices branching. Stems 1–10+, ascending to erect, proximally glabrous, strigose in arrays. Leaves: basal and proximal cauline petiolate, blades narrowly oblanceolate, (20–) 50–100 (–160) × (2–) 5–16 (–56) mm, margins serrate to crenate, apices acute to obtuse, glabrous; mid and distal sessile, similar, blades lanceolate to linear, 12–45 × 2–19 mm, reduced distally, margins entire to sparsely serrate, sometimes resinous. Heads 3–150, not secund, in narrowly elongate, paniculiform arrays, broadly so in robust plants (12.5–19 × 2.5–3 cm wide), consisting of short axillary and terminal racemiform clusters, proximal branches elongate in larger plants, branches glabrate to strigillose. Peduncles 3.1–10.3 mm, glabrate to sparsely strigillose; bracteoles few, linear. Involucres campanulate, 3–7 mm. Phyllaries (in 3–4 series) strongly unequal, often resinous; outer ovate, acute, inner linear-oblong, obtuse. Ray-florets 7–16; laminae 2–5 × 0.7–0.9 mm. Disc-florets 6–31; corollas 4–4.9 mm, lobes 0.6–1.3 (–2) mm. Cypselae narrowly obconic, 1.9–3.2 mm, sometimes with dark ridges, strigillose; pappi 1.9–5.2 mm (bristles sometimes clavate).
Distribution
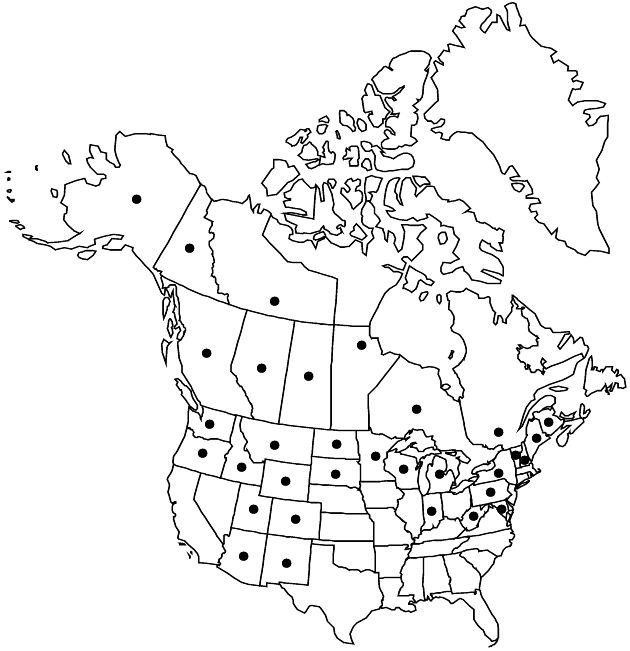
Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., N.W.T., Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Ariz., Colo., Idaho, Ind., Maine, Mass., Md., Mich., Minn., Mont., N.Dak., N.H., N.Mex., N.Y., Oreg., Pa., S.Dak., Utah, Vt., W.Va., Wash., Wis., Wyo., Mexico
Discussion
Varieties 7 (7 in the flora).
The somewhat viscid-resinous heads of Solidago simplex are its most distinctive feature, separating it from similar sympatric species. G. S. Ringius (1985) did a detailed multivariate analysis of the S. spathulata/S. simplex complex (the latter under the name S. glutinosa). The cytogeography of the species complex was presented by Ringius and J. C. Semple (1987). Neither study included data on the next three species occurring in the southeastern United States.
The species is divided into two subspecies and seven varieties following G. S Ringius (1985) and J. C. Semple et al. (1999). Three varieties occur in the diploid transcontinental subsp. simplex: var. simplex, var. nana, and var. chlorolepis. Four varieties occur in the eastern North American tetraploid-hexaploid subsp. randii: var. monticola, var. gillmanii, var. ontarioensis, and var. racemosa. Except for var. simplex, varieties are restricted to different habitats in relatively limited ranges.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Basal and cauline leaves spatulate to orbiculate, apices obtuse to rounded; cypselae moderately to densely strigose (S. simplex subsp. simplex) | > 2 |
| 1 | Basal and cauline leaves spatulate to obovate, apices usually acute; cypselae sparsely to moderately strigose (S. simplex subsp. randii) | > 5 |
| 2 | Cauline leaves 5–16 (longest 60+ mm); w North America, disjunct along shores of upper Great Lakes and in s Quebec | Solidago simplex var. simplex |
| 2 | Cauline leaves 2–7 (longest to 60 mm); alpine slopes, w North America, Mt. Albert, Gaspé, Quebec | > 3 |
| 3 | Shortest phyllaries 1.4–2 mm; disc corollas 3.9–4.2 mm; serpentine soils, Mt. Albert, Gaspé, Quebec | 5a.Solidago simplex var. chlorolepis |
| 3 | Shortest phyllaries 2.1–3.1 mm; disc corollas 4.2–5.4 mm; alpine slopes, Rocky Mountains, Cascade Mountains, Vancouver Island. | > 4 |
| 4 | Basal leaves usually spatulate, rarely broadly elliptic, proximal blades gradually attenuated to winged petioles, margins weakly crenate; alpine slopes, Rocky Mountains | Solidago simplex var. simplex |
| 4 | Basal leaves orbiculate to broadly elliptic, proximal blades abruptly attenuated to winged petioles, margins distinctly crenate; alpine slopes of Cascade Mountains, Vancouver Island | 5a.Solidago simplex var. nana |
| 5 | Proximal cauline leaves spatulate to obovate, (5–)10–42 mm wide; leaf margins often sharply serrate | > 6 |
| 5 | Proximal cauline leaves lanceolate to narrowly spatulate, 2–10(–21.5) mm wide; leaf margins entire or dentate, rarely serrate | > 7 |
| 6 | Plants (10–)18–53(–83) cm, arrays tending to be compact, virgate; proximal cauline leaves (5–)10–22(–31) mm wide, margins crenate to serrate; barren, rocky, non-alpine uplands; se Quebec, New England, New York | 5b.Solidago simplex var. monticola |
| 6 | Plants (20–)38–73(–84) cm, robust, arrays tending to be paniculiform; proximal cauline leaves (6–)7.5–24(–42) mm wide, margins often sharply serrate; sand dunes, Lake Michigan, n Lake Huron | 5b.Solidago simplex var. gillmanii |
| 7 | Cauline leaves (3–)12–33(–58); peduncle bracteoles 2+; calcareous rocky riverbanks, e Quebec s to West Virginia and Maryland | 5b.Solidago simplex var. racemosa |
| 7 | Cauline leaves (2–)4–13(–24); peduncle bracteoles 1–3(–4); rocky shores, Lake Superior, n Lake Huron | 5b.Solidago simplex var. ontarioensis |