Calamagrostis tweedyi
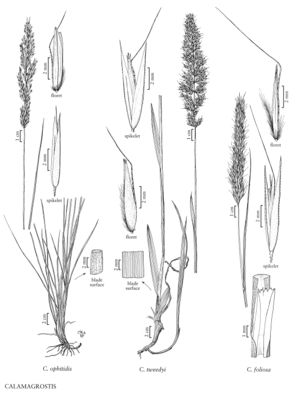
Plants without sterile culms; loosely cespitose, with rhizomes 1-10 cm long, 2-4 mm thick. Culms (47) 60-120 (150) cm, unbranched, smooth, rarely slightly scabrous; nodes 2-3. Sheaths and collars smooth; ligules (1) 3.5-6 (8) mm, obtuse, lacerate; blades (3) 4-20 (38) cm long, (2) 3-8 (13) mm wide, culm blades wider than 6 mm, flat, abaxial surfaces smooth, adaxial surfaces smooth or slightly scabrous, glabrous or sparsely hairy. Panicles 7-16 (19) cm long, (1) 1.5-2 cm wide, erect, usually contracted, sometimes interrupted near the base, pale-purple to purple; branches (0.2) 2.4-6.7 (7.7) cm, smooth, sometimes sparsely scabrous distally, spikelet-bearing to the base. Spikelets (4.5) 5.5-8 (9) mm; rachilla prolongations (0.5) 1-2 (4) mm, hairs 1.5-3 mm. Glumes keeled, smooth or the keels scabrous, lateral-veins prominent, apices acute; callus hairs 0.8-1 mm, 0.2-0.3 times as long as the lemmas, sparse; lemmas (4) 4.5-6.5 (7.5) mm, 0-1.5 mm shorter than the glumes, scabridulous; awns 6-8 mm, attached to the lower 1/5 – 3/10 of the lemmas, exserted more than 2 mm, stout, easily distinguished from the callus hairs, bent; anthers 2-3.5 mm. 2n = unknown.
Distribution
Mont., Idaho, Wash.
Discussion
Calamagrostis tweedyi grows in montane to subalpine moist meadows and coniferous forests, often in association with Carex geyeri, at 900-2000 m. Its range extends from Washington and Oregon to western Montana.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.