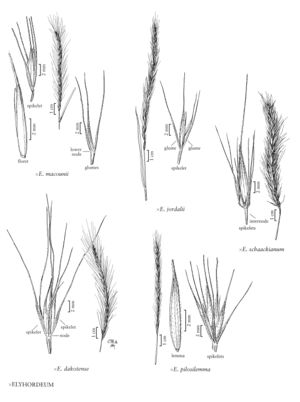
×elyhordeum macounii
Culms 50-100 cm. Sheaths usually glabrous; ligules truncate; blades 9-16 cm long, 2-5 mm wide, stiff, ascending, scabrous. Spikes 4-13 cm long, about 5 mm wide, erect, lower nodes with 1-2 spikelets, upper nodes with 1 spikelet, the spikelets imbricate. Spikelets with 1-3 florets, those at the lower nodes frequently with 3 glumes. Glumes 6-9 mm, not indurate at the base, awned, awns as long as or longer than the glume bodies; lemmas 6-11 mm, oblong-lanceolate, glabrous or sometimes scabrous distally, awned, awns 10-20 mm. 2n = 28.
Distribution
Wyo., Colo., Alaska, Oreg., Wash., Mont., Utah, Minn., Idaho, Kans., N.Dak., Nebr., S.Dak., Ill., Iowa, Mo., Alta., B.C., Man., N.W.T, Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Calif., Nev., N.Mex.
Discussion
×Elyhordeum macounii consists of hybrids between Elymus trachycaulus and Hordeum jubatum. It is quite common in western and central North America. Backcrosses to E. trachycaulus may have non-disarticulating rachises; they are likely to be identified as E. trachycaulus, falling between subsp. trachycaulus and subsp. subsecundus. Artificial, partially fertile octoploids were distributed to natural and experimental areas in several western states prior to 1960 (Bowden 1960); it is not known whether they have persisted.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.