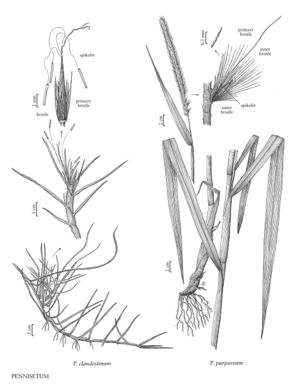
Pennisetum clandestinum
Plants perennial; rhizomatous and stoloniferous. Culms 3-45 cm, decumbent, highly branching; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous or pubescent; ligules 1.3-2.2 mm; blades 1-15 cm long, 1-6 mm wide, flat or folded, glabrous or pubescent. Panicles 2-2.7 cm, axillary, concealed in the sheaths; rachises flat, glabrous or scabrous. Fascicles 1-6; axes to 0.5 mm, with 1-2 spikelets; outer and inner bristles alike, 6-15, 0.5-10.9 mm; primary bristles 10-14 mm, usually not noticeably longer than the other bristles. Spikelets 10-22 mm, sessile or pedicellate, pedicels to 0.2 mm; lower glumes usually absent, sometimes to 0.5 mm, veinless; upper glumes 0-1.3 (3.5) mm, veinless; lower florets sterile; lower lemmas 10-22 mm, 9-13-veined; lower paleas usually absent; upper lemmas 10-22 mm, 8-12-veined; upper paleas 2-7-veined; anthers 4.7-7 mm, long-exserted from the florets at anthesis. 2n = 36.
Distribution
Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands, Calif., Pacific Islands (Hawaii)
Discussion
Pennisetum clandestinum is native to Africa. It now grows in many parts of the world, often as a forage or lawn grass. The U.S. Department of Agriculture considers it a noxious weed. In parts of the Flora region, it is well-established in lawns.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.