Leptochloa panicoides
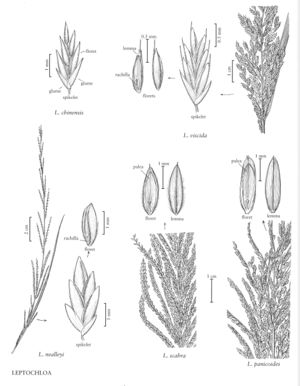
Plants annual. Culms (7) 45-110 cm, often geniculate below, usually ascending to erect above, rarely branching at the base, often branching distally; internodes hollow. Sheaths glabrous, margins occasionally sparsely ciliate on the basal 1/2; ligules 2.2-3.8 mm, membra¬nous, truncate, somewhat erose; blades 4-20 cm long, 4-8 mm wide, both surfaces smooth or scabridulous. Panicles 20-35 cm, with 20-30 (90) racemose branches; branches 2.5-7 cm, ascending, mostly stiff. Spikelets 4-5 mm, usually somewhat imbricate, with 4-6 (7) florets. Lower glumes 0.9-1.9 mm, usually lanceolate, sometimes falcate, acute; upper glumes 1.8-2.3 mm, ovate, acute to obtuse; lemmas 2.4-3 mm, narrowly elliptic to ovate, membranous, midveins and lateral-veins sericeous basally, lateral-veins prominent, excurrent, apices acute to broadly acute, unawned, sometimes mucronate; paleas glabrous; anthers 3, 0.6-0.8 mm. Caryopses 1.1-1.4 mm long, 0.7 mm wide, elliptic, depressed obovate in cross-section. 2n = 20.
Distribution
Puerto Rico, Va., Miss., Tex., La., Mo., Ala., Tenn., Ark., Ill., Ga., Ind., Ky., Fla.
Discussion
Leptochloa panicoides is native from the central Mississippi and Ohio river drainages south through Mesoamerica to Brazil. It usually grows in somewhat mesic habitats. It has been reported from two counties in Texas, but no specimens documenting the reports have been found so they are not shown.
Nicora (1995) merged Leptochloa panicoides with L. scabra, but the two differ consistently in the number of panicle branches, spikelet length, and prominence of the lemma veins.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.