Quercus hinckleyi
Contr. Texas Res. Found., Bot. Stud. 1: 40. 1951.
Shrubs, evergreen, low, to 0.75 (-1.5) m, spreading rhizomatously in thickets, intricately branched. Bark gray, scaly. Twigs light-brown, pruinose, becoming waxy-glaucous in 2d season, 1-1.5 mm diam., glabrous or sparsely and minutely stellate-pubescent. Buds minute, subrotund, 0.5-1 mm; scales reddish-brown, glabrous except for ciliate margins. Leaves: petiole to 2 mm. Leaf-blade subrotund or rotund, to 15 × 15 mm, thick, leathery, base cordate or auriculate, margins strongly crisped with 2-3 coarse, spinescent teeth on each side, cartilaginous-thickened secondary-veins obscure, apex acute or obtuse, spine-tipped; surfaces abaxially blue-green, glaucous, glabrous, microscopically markedly papillose, adaxially blue-green, glaucous, glabrous, secondary-veins slightly raised on both surfaces. Acorns solitary, subsessile or on axillary peduncle to 4 mm; cup shallow, saucer-shaped, 1-3 mm deep × 10-15 mm wide, enclosing base of nut only, margin irregularly undulate, scales closely appressed, minute, basally tuberculate-thickened, glabrous except for thin ciliate margins; nut ovoid, 10-20 × 8-12 mm, glabrous. Cotyledons distinct.
Phenology: Flowering spring.
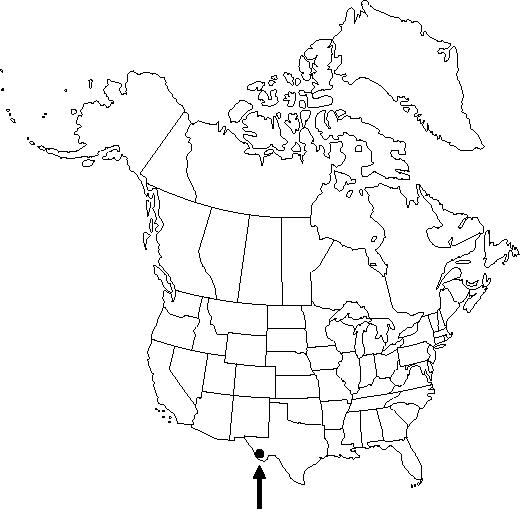
Habitat: On dry desert slopes
Elevation: 1150-1400 m
Discussion
Of conservation concern.
This species is known only from two sites in the United States, El Solitario and near Shafter, Texas. The Shafter population includes some individuals with characteristics that suggest hybridization with Quercus pungens Liebmann. These plants are larger, with more pubescent twigs and leaves, and hemispheric acorn cups to 10 mm deep. Such plants have recently been collected in adjacent Mexico. Fossil evidence from packrat middens indicates Q. hinckleyi probably had a broader distribution and was a dominant shrub between 19,000 and 9500 years ago.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
No values specified.