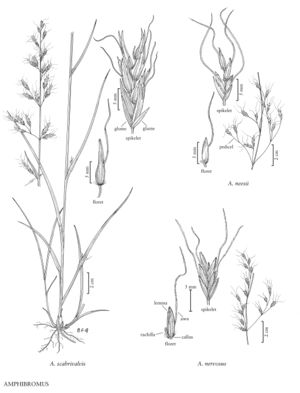
Amphibromus neesii
Plants perennial; usually cespitose, occasionally rhizomatous. Culms 30-150 cm tall, 1-2.5 mm thick, erect, terete to flattened, glabrous; nodes 2-4; lowest internodes not swollen. Sheaths smooth or scabridulous, ribbed; ligules 4.5-8 mm, acute to acuminate; blades 10-20 (37) cm long, 2-4 mm wide, flat or involute, smooth to scabrous, abaxial surfaces scabridulous, adaxial surfaces deeply ribbed, scabrous. Terminal panicles 15-40 cm, erect, sparse, lower portion rarely partially enclosed in the uppermost sheaths; branches usually 7-14 cm, ascending or appressed, often flexuous; pedicels usually 10-20 mm. Spikelets 8-17 mm, with 2-6 florets. Glumes unequal, green, sometimes purplish in the center, with hyaline margins; lower glumes 3.5-6.5 mm, 3-5-veined; upper glumes 4.5-7.5 mm, 5-7-veined; lemmas 5-8.4 mm, 7-veined, papillose to scabrous, apices appearing constricted, 2-4-toothed, awned from the upper 2/3 - 3/4 of the lemmas, awns 14-26 mm, geniculate and twisted; paleas 8/10 – 9/10 the length of the lemmas, papillose; anthers of chasmogamous florets 1.3-2.3 mm. 2n = unknown.
Discussion
Amphibromus neesii is an Australian species that grows on floodplains and river banks, and in marshes and lagoons. It was first reported as growing in North America in 1990; examination of the voucher specimens showed them to be A. nervosus, which differs from A. neesii in having a lower lemma awn insertion. Both species are included in this treatment to help prevent future misidentification of the two species in North America.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.