Asarum
Sp. Pl. 1: 442. 175.
Gen. Pl. ed. 5, 201. 1754.
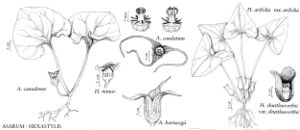
Herbs, perennial, deciduous, rhizomatous, without aerial stems. Leaves alternate (sometimes appearing opposite because of crowding), 2-ranked; stipules absent; petiolate foliage leaves and sessile, triangular scale-leaves both present. Leaf-blade membranous or leathery, pubescent at least abaxially and on margins. Inflorescences terminal on rhizome, flowers solitary; bracts absent. Flowers: sepals distinct, usually mixture of white, green, tan, red, or purple, proximally touching valvately and forming well-de tube, externally usually villous, inner surface strigose, smooth or with weak longitudinal ribs, never with network of low ridges; vestigial petals present or absent; stamens 12, distinct; filaments longer than pollen-sacs; terminal appendage of anther well developed; ovary inferior, 6-locular; styles connate in column. Capsule fleshy, dehiscence irregular. Seeds ovoid, not winged, with fleshy appendage. x = 13.
Distribution
North America, Eurasia
Discussion
Species ca. 10 (6 in the flora).
The species seem amply distinct, but herbarium material can be difficult to key for several reasons. First, the diagnostic colors of some organs (especially of the connective and the inner hairs of the calyx) often darken on drying. Second, immature flowers and young fruit are superficially similar to mature flowers, but color and posture of floral organs may be different at those stages. For instance, posture of the distal portion of sepals at anthesis (whether erect, spreading, or reflexed) is diagnostic for the species, but sepals in all species are erect in bud and in fruit. Third, as in Hexastylis, distortion of the flower in pressing makes it difficult to interpret calyx structure. In particular, the distinction between proximal portions of the sepals, which meet valvately to form a well-defined false calyx tube, and distal portions, which do not, is obvious in fresh material but often unclear in the herbarium.
The flowers of Asarum are predominantly self-pollinated, but they are occasionally visited by mycotrophic flies (K. L. Lu 1982).
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Adaxial leaf surface almost always with white or silvery variegations; sterile tip of connective on inner stamens at least as long as pollen sacs; underground stems erect or ascending, deeply buried, internodes 0.2–1.5 cm. | > 2 |
| 1 | Leaf surface never variegate; sterile tip of connective on inner stamens shorter than (rarely about as long as) pollen sacs; rhizomes horizontal, shallow (deeply buried in A. wagneri), internodes 0.5–6.5 cm. | > 3 |
| 2 | False calyx tube subglobose, inner surface dark red with purple hairs; distal part of sepal tan or greenish (inner surface rarely red proximally), erect or spreading at anthesis, 17–52 mm; marginal hairs of leaf ± perpendicular. | Asarum marmoratum |
| 2 | False calyx tube cylindric, inner surface white with brownish purple stripes and white hairs (turning brown with age); distal part of sepal reddish, spreading perpendicularly or reflexed at anthesis (but erect in bud and fruit), 12–27 mm; marginal hairs of leaf strongly curved toward apex. | Asarum hartwegii |
| 3 | Flower descending; divergent part of sepal strongly reflexed at anthesis, 4–8 mm, acute to apiculate or short-acuminate. | Asarum lemmonii |
| 3 | Flower horizontal to erect; divergent part of sepal spreading or reflexed at anthesis, 6–75 mm, apiculate to acuminate or filiform-attenuate. | > 4 |
| 4 | Flowers horizontal; divergent part of sepal (11–)30–75 mm; leaves cordate. | Asarum caudatum |
| 4 | Flowers erect or ascending; divergent part of sepal 6–24 mm; leaves cordate-reniform to reniform. | > 5 |
| 5 | Adaxial surface of distal sepals purple; false calyx tube cylindric, outer surface usually tan or purplish; e North America. | Asarum canadense |
| 5 | Adaxial surface of distal sepals white or light green (at least distally); false calyx tube subglobose to cylindric-urceolate or urceolate, outer surface light green; s Oregon. | Asarum wagneri |
"broad" is not a number.