Avena barbata
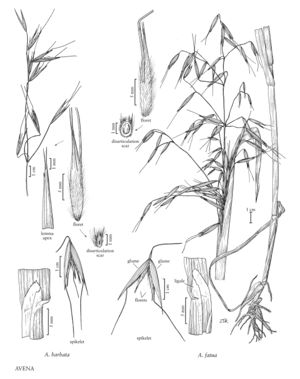
Plants annual. Culms 60-80 (150) cm, initially prostrate, usually becoming erect. Sheaths of the basal leaves pilose, upper sheaths usually glabrous; ligules 1-6 mm, obtuse; blades 6-30 cm long, 2-20 mm wide, glabrous or pilose. Panicles 15-35.5 (50) cm long, 6-12 cm wide, erect or nodding. Spikelets 21-30 mm, with 2-3 florets; disarticulation beneath each floret; disarticulation scars elliptic to triangular. Glumes subequal, 15-30 mm, 7-9-veined; calluses bearded, hairs 2-3 mm; lemmas 15-26 mm, densely strigose below midlength, apices acute, biaristate, 2 veins extending 2-4 mm beyond the apices, awns 30-45 mm, arising about midlength, geniculate; lodicules narrowly triangular, without lobes on the wings; anthers 2.5-4 mm. 2n = 28.
Distribution
Mass., N.Mex., Wash., Calif., Mont., Pacific Islands (Hawaii), Ariz., Oreg., Nev.
Discussion
Avena barbata is native to the Mediterranean region and central Asia. It has become naturalized in western North America, particularly California, displacing native grasses. It was collected once in Vancouver, British Columbia, but should be considered a waif there.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.