Cakile
Gard. Dict. Abr. ed. 4, vol. 1. 1754.
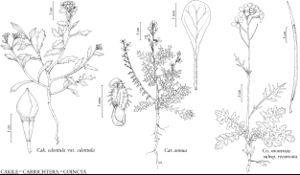
Annuals or, rarely, perennials; (succulent, taproot woody, with relatively long, horizontal roots); not scapose; glabrous or, sometimes, sparsely pubescent. Stems erect, ascending, prostrate, or divaricate, branched basally. Leaves cauline; usually petiolate, rarely sessile; blade (often fleshy), not rosulate, margins entire, crenate, dentate, sinuate, or pinnately lobed. Racemes considerably elongated in fruit. Fruiting pedicels (rachis) geniculate or not, slender or stout. Flowers: sepals erect, ovate or oblong, lateral pair saccate or not basally; petals (rarely aborted, reflexed), white to lavender, obovate to spatulate, claw differentiated from blade or not; stamens tetradynamous; filaments not dilated basally; anthers (introrse), ovate to oblong; nectar glands (4), distinct, median glands present. Fruits siliques or silicles, indehiscent, stipitate, segments 2, (fleshy and green becoming corky and dry), obovoid, oblong, fusiform, or lanceoloid, rarely hastate, (proximal segment) terete or laterally horned, (terminal segment) terete, 4-angled, or 8-ribbed; (segments each falsely 1-loculed, septum papery, appressed to one side, usually 1-seeded; proximal segment remaining attached to pedicel; terminal segment deciduous by transverse articulation, beaked); valves and replum not distinguishable; ovules (1 or) 2 (–4) per ovary; (style absent); stigma entire or slightly 2-lobed. Seeds aseriate or uniseriate, plump or flattened, not winged, (brown), oblong; seed-coat (smooth), not mucilaginous when wetted; cotyledons accumbent or incumbent, rarely contorted. x = 9.
Distribution
North America, Mexico, West Indies, Central America, Europe, Asia (Near East), n Africa, in e Asia (Japan), Australia
Discussion
Species 7 (5 in the flora).
Cakile is common on sandy beaches of the North Atlantic Ocean, the Baltic, Black, Mediterranean, North, and White seas, the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico, and the Great Lakes, and is naturalized in Australia, Japan, and on the Pacific Coast of North America; one species, C. arabica Velenovsky & Bornmüller, is found in deserts of the Middle East (s Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia).
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Proximal fruit segments with 2 opposite, lateral horns distally; leaf blades broadly ovate to lanceolate, margins sinuately lobed or deeply pinnatifid; petals 3-6 mm wide, usually lavender, rarely white. | Cakile maritima |
| 1 | Proximal fruit segments without lateral horns distally; leaf blades ovate, ovate-lanceolate, or spatulate, margins entire, dentate, sinuate, crenate, or pinnatisect; petals 1.2-4.5 mm wide, white or lavender | > 2 |
| 2 | Plants usually sprawling; leaf blades not especially fleshy; racemes often 3+ dm; petals usually white, rarely lavender, 3-4.5 mm wide. | Cakile lanceolata |
| 2 | Plants not or, rarely, sprawling (erect to prostrate); leaf blades usually fleshy; racemes 1-2 dm; petals lavender to white, less than 3 mm wide | > 3 |
| 3 | Rachises geniculate in fruit; petals 1.2-1.9 mm wide. | Cakile geniculata |
| 3 | Rachises not geniculate in fruit; petals 1.3-3 mm wide | > 4 |
| 4 | Fruits terete to 4-angled, 3-4 mm wide; beak conic, apex acute. | Cakile constricta |
| 4 | Fruits 8-ribbed, or 4-angled, 5-9 mm wide; beak flattened, apex usually retuse or blunt, rarely acute. | Cakile edentula |
"elongated" is not a number."thick" is not a number.