Chamaebatia foliolosa
Pl. Hartw., 308. 1849.
Plants 1–5 (–7) dm, forming extensive colonies. Stems: internodes 5–10 (–15) mm; bark reddish-brown. Leaves 3-pinnately compound; petiole 10 (–15) mm; blade obovate to obtrullate, (28–) 45–70 (–94) × (13–) 20–45 (–71) mm, surfaces moderately hirtellous, sparsely stipitate-glandular; rachises straight; pinnae (8–) 10–12 per side, oblong to oblong-obovate, (3–) 10–25 (–40) × (1.8–) 3–8 (–13) mm; pinnules (4–) 7–10 per side, oblong, (1.2–) 2.5–5 (–10) × (0.6–) 1.5–3 (–5) mm, each pinnately divided into (3–) 5–11 pairs of segments, segments oblong-obovate to obovate, (0.3–) 0.6–1.5 × (0.2–) 0.5–1 mm, terminal largest, each with terminal short-stipitate gland, adaxial rachis and rachilla with additional segments between pinnae and pinnules. Inflorescences (3–) 5–7 (–10) -flowered, panicles, 35–60 (–80) mm; peduncles 2–5 mm. Flowers: hypanthium 4–6 mm; hypanthia and sepals pubescent, stipitate-glands 0.8–1.5 mm; sepals oblong-lanceolate, 4.5–6 (–7) mm, apex acute; petals 6–9 mm; stamens 55–65 (–76); styles 5.5 mm. Achenes 4.5–5.5 mm. 2n = 18.
Phenology: Flowering Apr–Jun.
Habitat: Slopes, flats, coarse sands, yellow pine to montane conifer forests
Elevation: (300–)600–1800(–2300) m
Discussion
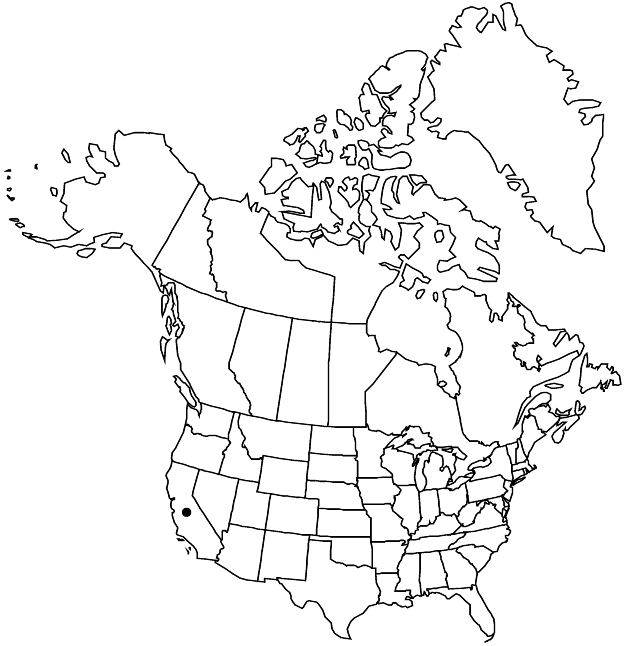
Chamaebatia foliolosa occurs on the western slope of the Sierra Nevada and into the Cascade Range, from Shasta to Inyo and Kern counties.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"dm" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.