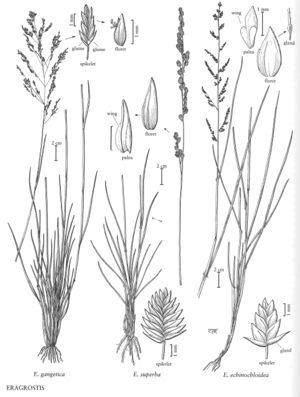
Eragrostis echinochloidea
Plants perennial; cespitose, with innovations. Culms 30-100 cm, erect to geniculate, with narrow, sunken glandular bands. Sheaths sometimes glandular, apices hairy, hairs to 5 mm; ligules 0.4-1 mm; blades 5-21 cm long, 2-6 (7) mm wide, flat to involute, with small crateriform glands on the keels and veins, sparsely pilose adaxially. Panicles 4-19 cm long, 0.8-7 cm wide, oblong to ovate, glomerate, spikelets clustered in 1-sided groups; primary branches 0.5-7.5 cm, diverging 10-90° from the rachises, angled, sinuous, glandular; pulvini hairy, hairs to 2 mm; pedicels 0.2-2 mm, stout, erect, without a narrow band or abscission line near the apices. Spikelets 2-5 mm long, 2-3.5 mm wide, broadly ovate, greenish, stramineous to plumbeous, with 7-14 florets; disarticulation basipetal, glumes persistent. Glumes subequal, 1.7-2.2 mm, ovate, membranous, keels with small crateriform glands, apices acute to acuminate; lemmas 1.8-2.3 mm, broadly ovate to orbicular, chartaceous, keels with small crateriform glands, apices acute to obtuse; paleas 1.7-2.2 mm, chartaceous, each side with a broad wing at the base, wings often projecting beyond the lemma bases, apices acute; anthers 3, 0.5-0.9 mm, yellowish. Caryopses 0.8-1.1 mm, ellipsoid, reddish-brown. 2n = 30.
Distribution
Ariz.
Discussion
Eragrostis echinochloidea is native to southern Africa. It is now established in Arizona, growing in gravel soils, often along roadsides and in sidewalks, from 700-1000 m. It has also been found in Prince George's County, Maryland.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.