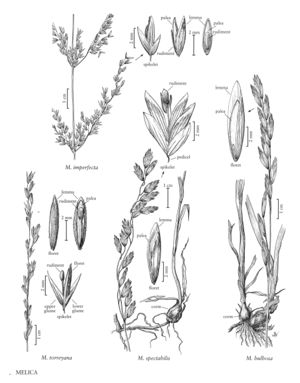
Melica spectabilis
Plants loosely cespitose, rhizomatous. Culms 45-100 cm, form¬ing corms, corms connected to the rhizomes by a rootlike, 10-30 mm structure, which usually remains attached to the corm; internodes smooth. Sheaths usually glabrous, often pilose at the throat and collar; ligules 0.1-2 mm; blades 2-5 mm wide, abaxial surfaces scabridulous over the veins, adaxial surfaces usually glabrous. Panicles 5-26 cm; branches 2-5 cm, usually appressed, sometimes divergent and flexuous, with 2-3 spikelets; pedicels not sharply bent; disarticulation above the glumes. Spikelets 7-19 mm, with 3-7 bisexual florets, base of the distal florets concealed at anthesis; rachilla internodes 1-2 mm, not swollen when fresh, not wrinkled when dry. Glumes usually less than 1/2 the length of the spikelets; lower glumes 3.5-6.4 mm long, 1.5-3 mm wide, 1-3-veined; upper glumes 5-7 mm long, 2.3-3.5 mm wide, 5-7-veined; lemmas 6-9 mm, glabrous, scabridulous, 5-11-veined, veins inconspicuous, apices rounded to acute, unawned; paleas about 73 the length of the lemmas; anthers 1.5-3 mm; rudiments 1.5-3.5 mm, acute, distinct from the bisexual florets, sometimes surrounded by a small sterile floret similar in shape to the bisexual florets. 2n= 18.
Distribution
Colo., Wash., Utah, Alta., B.C., Idaho, Mont., Wyo., Calif., Nev., Oreg.
Discussion
Melica spectabilis grows in moist meadows, flats, and open woods, from 1200-2600 m, primarily in the Pacific Northwest and the Rocky Mountains. It is often confused with M. bulbosa, differing in its shorter glumes, "tailed" corm, and the more marked and evenly spaced purplish bands of its spikelets.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.