Melica subulata
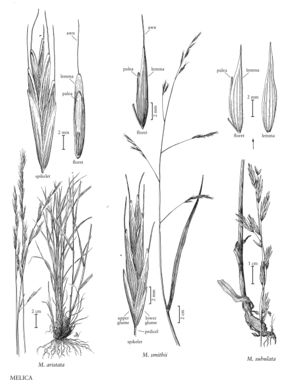
Plants cespitose, rhizomatous. Culms 55-125 cm, forming corms, corms attached to the rhizomes; internodes scabridulous basally. Sheaths usually scabridulous, sometimes glabrous or pilose; ligules 0.4-5 mm, to 1.5 mm on the lower leaves, to 5 mm on the upper leaves; blades 2-10 mm wide, abaxial surfaces smooth or scabridulous, adaxial surfaces scabridulous, glabrous or with hairs. Panicles 8-25 cm, lax; branches 1.7-9 cm, usually appressed to ascending, occasionally divergent, with 1-5 spikelets; pedicels not sharply bent; disarticulation above the glumes. Spikelets 10-28 mm, with 2-5 bisexual florets; rachilla internodes 1.8-2 mm. Lower glumes 4-8 mm long, 1.3-2.2 mm wide, 1-3-veined; upper glumes 5.5-11.5 mm long, 2-3 mm wide, 3-5-veined; lemmas 5.5-18 mm, usually strigose over the veins, hairs longest towards the base, 7-9-veined, veins prominent, apices strongly tapering and acuminate, unawned; paleas 1/2 - 3/4 the length of the lemmas; anthers 1.5-2.5 mm; rudiments 4-9 mm, tapering, resembling the bisexual florets. Caryopses 4-5 mm. 2n = 18.
Distribution
Alaska, Colo., Idaho, Nev., S.Dak., Wash., Wyo., Alta., B.C., Mont., Calif., Oreg.
Discussion
Melica subulata grows from sea level to 2300 m in mesic, shady woods. Its range extends from the Aleutian Islands of Alaska through British Columbia to California, east to Lawrence County, South Dakota, and into Colorado.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.