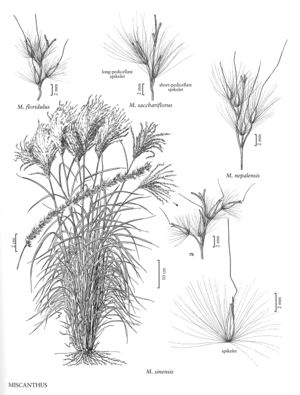
Miscanthus sinensis
Plants cespitose, forming large clumps, with short, thick rhizomes. Culms 60-200 cm tall, 3-7 mm thick below. Leaves predominantly basal; sheaths mostly glabrous, throats pilose; ligules 1-2 mm; blades 20-70 cm long, 6-20 mm wide, midveins conspicuous abaxially, 1-2 mm wide, whitish. Panicles 15-25 cm long, 8-28 cm wide, dense to loose, usually with more than 15 branches; rachises 6-15 cm, 1/3 – 2/3 as long as the inflorescences; branches 8-15 (30) cm long, about 10 mm wide, sometimes branched at the base; internodes 4-8 mm, glabrous. Shorter pedicels 1.5-2.5 mm; longer pedicels 3.5-6 mm, slightly recurved at maturity. Spikelets 3.5-7 mm, lanceolate to lanceovate; callus hairs 6-12 mm, to twice as long as the spikelets, white, stramineous to reddish. Glumes subequal; lower glumes 3-veined, ciliolate on the margins; upper glumes 1-veined; awns of upper lemmas 6-12 mm, geniculate below. 2n = 38, 40, and dysploids from 35-42.
Distribution
Conn., N.J., N.Y., Del., D.C., W.Va., Fla., Mass., R.I., La., Tenn., Pa., Va., Colo., Ont., Calif., Ala., Ill., Ga., Md., Ohio, Mo., Mich., Miss., Ky., N.C., S.C.
Discussion
Miscanthus sinensis is native to southeastern Asia. It is frequently cultivated in the United States and southern Canada, and is now established in some parts of the United States. Approximately 40 forms and cultivars are available, some having white-striped leaves, others differently colored callus hairs and, consequently, differently colored panicles.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number."fine" is not a number."thick" is not a number.