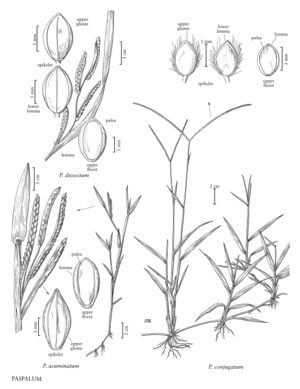
Paspalum acuminatum
Plants perennial; rhizomatous. Culms 30-100 cm, strongly decumbent, upright portion usually not standing more than 20 cm tall, much branched; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous; ligules 1-2.4 mm; blades to 7 cm long, 3-6.5 mm wide, flat. Panicles terminal, with 2-5 racemosely arranged branches; branches 2-6 cm, diverging, persistent; branch axes 2-3.3 mm wide, broadly winged, glabrous, margins scabrous, terminating in a spikelet. Spikelets 3.2-4 mm long, 1.6-1.7 mm wide, solitary, appressed to the branch axes, elliptic, abruptly pointed, stramineous. Lower glumes absent; upper glumes and lower lemmas glabrous, 5-veined; upper florets stramineous, lemmas with a few minute hairs at the apices. Caryopses 2-3 mm, white. 2n = 40.
Distribution
Ga., Tex., La., Ala., Miss., Fla.
Discussion
Paspalum acuminatum grows at the edges of lakes, ponds, rice fields, and wet roadside ditches. It is native to the Americas, with a range that extends from the southern United States to Argentina.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.