Paspalum notatum
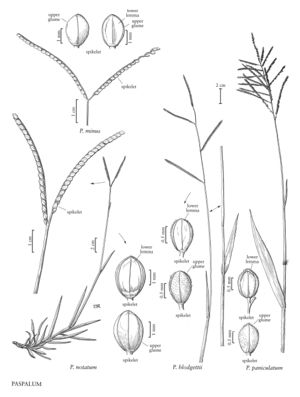
Plants perennial; rhizomatous. Culms 20-110 cm, erect; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous or pubescent; ligules 0.2-0.5 mm; blades 5-31 cm long, 2-10 mm wide, flat or conduplicate, glabrous or pubescent. Panicles terminal, usually composed of a digitate pair of branches, 1-3 additional branches sometimes present below the terminal pair; branches 3-15 cm, diverging to erect; branch axes 0.7-1.8 mm wide, narrowly winged, glabrous, margins scabrous, terminating in a spikelet, distal spikelets sometimes reduced. Spikelets 2.5-4 mm long, 2-2.8 mm wide, solitary, appressed to the branch axes, broadly elliptic to ovate or obovate, glabrous, light stramineous to white, apices obtuse to broadly acute. Lower glumes absent; upper glumes glabrous, 5-veined; lower lemmas 5-veined, margins inrolled; upper florets light yellow to white. Caryopses 2-3 mm, white. 2n = 20, 30, 40.
Distribution
Tenn., N.J., Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands, Okla., Miss., Tex., La., Calif., N.C., Ala., Ark., Pacific Islands (Hawaii), S.C., Va., Ill., Ga., Fla.
Discussion
Paspalum notatum is native from Mexico through the Caribbean and Central America to Brazil and northern Argentina. It was introduced to the United States for forage, turf, and erosion control. It is now established, generally being found in disturbed areas and at the edges of forests in the southeastern United States.
Paspalum notatum is sometimes treated as having distinct varieties. They are not recognized here because the variation among them is continuous. A number of cultivars have been developed for use as turf grasses; among these cultivars are 'Common Bahiagrass', 'Pensacola Bahiagrass', and 'Argentine Bahiagrass'.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.