Pennisetum alopecuroides
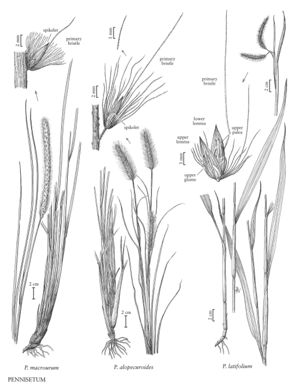
Plants perennial; cespitose. Culms 30-100 cm, erect; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous, margins ciliate; ligules 0.2-0.5 mm, membranous, ciliate; blades (10) 30-60 cm long, 2-8 (12) mm wide, flat to folded, glabrous, margins ciliate basally. Panicles all terminal, 6-20 cm long, 20-53 mm wide, fully exerted from the sheaths, erect, green to brown, deep purple, or stramineous to creamy-white; rachises terete, with pubescent hairs. Fascicles 9-16 per cm; fascicle axes 1.5-5.6 mm, with a stipelike base of 1-5.6 mm and 1 (2) spikelet (s); outer bristles 13-19, 0.8-15.6 mm; inner bristles 7-10, 11.2-30 mm, scabrous; primary bristles 26.7-35 mm, scabrous, usually not noticeably longer than the other bristles. Spikelets 5.5-8.4 mm, sessile or subsessile, glabrous; pedicels to 0.1 mm; lower glumes 0.2-1.4 mm, veinless; upper glumes 2-4.9 mm, to 1/2 as long as the spikelet, 1-5-veined, acute to broadly acute; lower florets sterile; lower lemmas 4.9-8.1 mm, 7-9 (10) -veined; lower paleas absent; upper lemmas 5.2-7.6 mm, 5-7-veined, acuminate; anthers 3, 3-4.5 mm. 2n = 18.
Distribution
Pa., Ohio, N.C., N.Y., Ark., Ill.
Discussion
Pennisetum alopecuroides is native to southeast Asia. It is frequently grown as an ornamental in the Flora region.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.