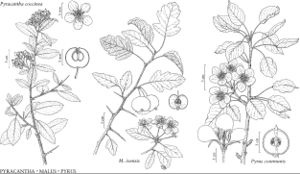
Pyrus communis
Sp. Pl. 1: 479.
2: 1200. 1753.
Plants 50–150 (–300) dm. Branches grayish brown or dark reddish-brown, glabrous; short-shoots of young plants often thorn-tipped. Leaves: petiole 1.5–5 cm, slightly pubescent when young; blade ovate or suborbiculate to elliptic, 2–5 (–7) × 1.5–2.5 cm, base broadly cuneate to almost rounded, margins obtusely serrate, serrulate, or crenulate, sometimes entire, densely ciliate when young, apex acute or shortly acuminate, surfaces pubescent when young, glabrescent. Pedicels 2–3.5 cm, pubescent or glabrate. Flowers 25–35 mm diam.; sepals triangular-lanceolate, 5–9 × 3–4 mm, apex acuminate; petals white, obovate, (12–) 13–15 × 10–13 mm; ovaries 5-locular; styles (3–) 5. Pomes green, yellowish, or reddish green, globose, subglobose, ovoid, or pyriform, 30–160 × 15–120 mm; sepals persistent. 2n = 34.
Phenology: Flowering Mar–May; fruiting Jul–Aug.
Habitat: Open woods, old fields, clearings, fencerows
Elevation: 0–1000+ m
Distribution
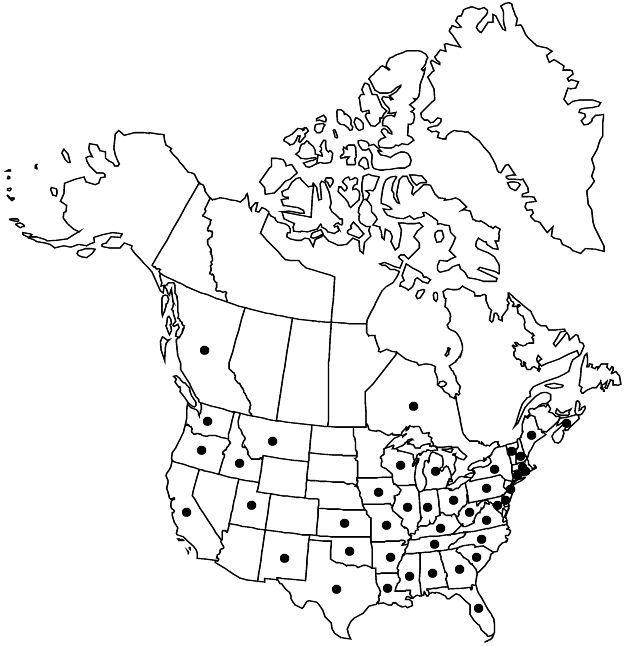
Introduced; B.C., N.S., Ont., Ala., Ark., Calif., Conn., Del., Fla., Ga., Idaho, Ill., Ind., Iowa, Kans., Ky., La., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Miss., Mo., Mont., N.H., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Okla., Oreg., Pa., R.I., S.C., Tenn., Tex., Utah, Vt., Va., Wash., W.Va., Wis., Eurasia, also in Mexico
Discussion
Pyrus communis is frequently cultivated and escapes to adjacent habitats, where it is sometimes common or even dominant. It includes more than a thousand cultivars, most of these being fruit (pomological) varieties. Ornamental forms with variegated leaves, dissected leaves, and unusual growth habits also occur. The taxon is of hybrid origin, and its parentage is thought to involve multiple species, including P. austriaca K. Kerner, P. nivalis Jacquin, P. pyraster, and P. syriaca Boissier. Pyrus pyraster is often treated as a wild species with smaller, rounder, and more sour fruit, yet it seems likely that wild pears fitting this description have originated from cultivated stock referable to P. communis, just as self-sown apples (Malus pumila) often have smaller, sour fruits. Recent authors are followed here in treating P. pyraster as a synonym.
The leaf margins of Pyrus communis are usually densely ciliate in flowering material, and this vestiture is retained to some extent in fruiting specimens. This characteristic, along with the broader fruiting pedicels, assists in distinguishing this species from P. cordata.
The high eating-quality pears were developed in the eighteenth or nineteenth century in northern Europe, although pears had been cultivated for centuries prior to that time. Currently, much of the cultivation in North America is in the Great Lakes area and on the Pacific coast. The highest production is in Europe (France, Germany, Switzerland), where most of the crop is used for making pear cider (perry); large-scale cultivation occurs also in Argentina, Australia, and Japan. The trees sometimes attain great age, and some in eastern North America, the French mission pears, persist today where planted 300 years ago on the sites of frontier forts in what was then a wilderness. Some of these old pears are of a type now no longer cultivated and have been identified as a significant germplasm resource.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"dm" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.