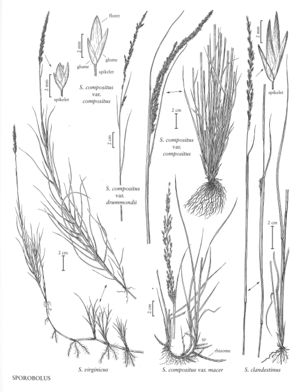
Sporobolus virginicus
Plants perennial; rhizomatous, stoloniferous. Culms 10-65 cm, erect to decumbent. Sheaths overlapping, margins ciliate, apices with tufts of hairs, hairs to 2 mm; ligules 0.1-0.4 mm; blades usually conspicuously distichous, 4-16 cm long, 2-5 mm wide, flat to loosely involute, glabrous abaxially, scabridulous adaxially, margins scabridulous. Panicles 3-10 cm long, 0.4-1.6 cm wide, contracted, spikelike, dense; primary branches 0.5-2 cm, appressed, spikelet-bearing to the base; pedicels 0.2-1.4 mm, appressed. Spikelets (1.8) 2-3.2 mm, yellowish-white to purplish-tinged, sometimes grayish. Glumes subequal, ovate-oblong, membranous; lower glumes 1.5-2.4 mm; upper glumes 1.8-3 (3.2) mm; lemmas 2.1-3 mm, ovate to lanceolate, membranous, glabrous, acute; paleas 2.1-3 mm, ovate, membranous; anthers 3, 1-1.7 mm, yellowish. Fruits not known. 2n = 20, 30.
Distribution
Puerto Rico, Md., Miss., Tex., La., Virgin Islands, Ala., N.C., S.C., Va., Pacific Islands (Hawaii), Ga., Fla.
Discussion
Sporobolus virginicus grows on sandy beaches, sand dunes, and in saline habitats, primarily along the south-eastern coast, occasionally inland. Its range extends through Mexico and Central America to Peru, Chile, and Brazil. No fruits of this species have been found despite examination of several natural populations and over 200 herbarium specimens.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.