Prunus mahaleb
Sp. Pl. 1: 474. 1753.
Shrubs or trees, not suckering, 30–150 dm, not thorny. Twigs with terminal end buds, densely puberulent. Leaves deciduous; petiole 4–20 mm, glabrous or ± puberulent on adaxial surface, sometimes glandular distally, glands 1–2, discoid; blade broadly ovate, oblong, or suborbiculate, 1.9–4.5 × 1.2–3.4 cm, base usually rounded to truncate, sometimes subcordate, margins crenate, teeth blunt, glandular, apex abruptly acuminate, apicula obtuse, surfaces usually glabrous, sometimes midribs and veins hairy abaxially. Inflorescences 4–10-flowered, corymbs; central axes 8–40 mm. Pedicels 6–18 mm (subtended by leafy bracts), glabrous. Flowers blooming at leaf emergence; hypanthium conic-campanulate, 2–3 mm, glabrous externally; sepals reflexed, oblong, 1.3–2 mm, margins entire, surfaces glabrous; petals white, elliptic to obovate, 6–7 mm; ovaries glabrous. Drupes dark red to black, ovoid, 6–10 mm, glabrous; mesocarps leathery; stones ellipsoid to subglobose, ± flattened. 2n = 16.
Phenology: Flowering Apr–May; fruiting Jun–Jul.
Habitat: Roadsides, stream banks, limestone bluffs and quarries, lowland thickets and woods, fencerows, chaparral
Elevation: 0–2300 m
Distribution
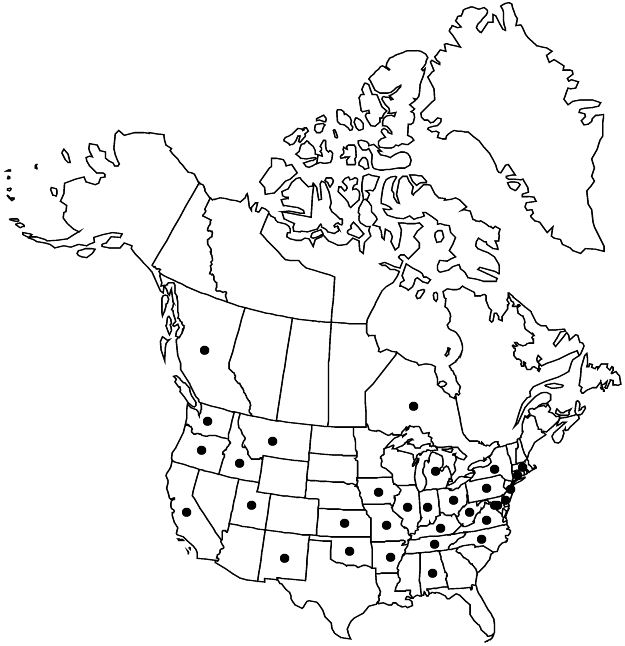
Introduced; B.C., Ont., Ala., Ark., Calif., Conn., Del., D.C., Idaho, Ill., Ind., Iowa, Kans., Ky., Md., Mass., Mich., Mo., Mont., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Okla., Oreg., Pa., Tenn., Utah, Va., Wash., W.Va., Eurasia
Discussion
Prunus mahaleb was introduced to North America as a rootstock for commercial cherries and is now sometimes cultivated for its attractive and fragrant flowers. At one time, the aromatic wood was a favorite for tobacco pipes.
Selected References
None.