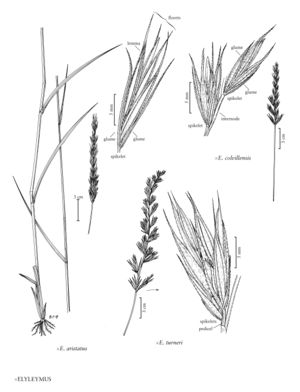
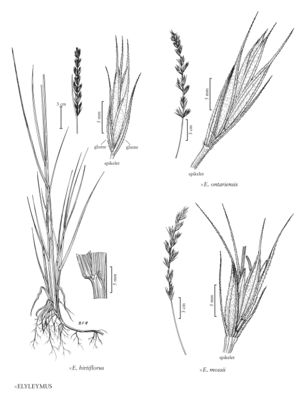
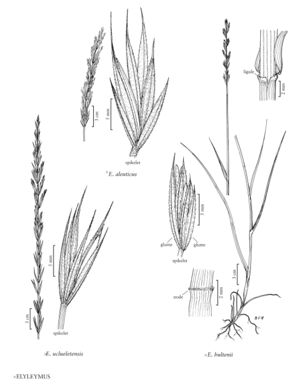
Plants perennial; sometimes rhizomatous. Culms 40-235 cm, erect. Inflorescences usually spikes, sometimes spikelike racemes, 5-35 cm, erect, with 1-3 spikelets per node, pedicels, when present, to 3 mm. Spikelets with 2-8 florets; disarticulation usually above the glumes and beneath the florets, sometimes below the glumes, sometimes in the rachises, usually tardy. Glumes linear to lanceolate, often awn-tipped; lemmas 6-25 mm, glabrous or hairy, usually awned, awns to 15 mm; anthers 1.5-5 mm.
Distribution
Colo., Wash., Alaska, Idaho, Alta., B.C., Ont., Que., Sask., Yukon, Wyo., Calif., Nev., Oreg.
Discussion
×Elyleymus consists of hybrids between Elymus and Leymus. So far as is known, they are completely sterile, having thin anthers (usually less than 0.5 mm thick) and failing to develop mature caryopses. Only the named hybrids are accounted for below. Each of the entities appears to be distinct, but identification of the parents is, in some instances, tentative. The descriptions are offered with considerable reservation, some being based solely on the type material. All the illustrations are based on type specimens.
The hybrids fall into two groups. Those with Leymus mollis as the Leymus parent (species 7-11) tend to have wider and flatter glumes than those with one of the inland species of Leymus as the Leymus parent.
Unless stated otherwise, measurements of the spikes include the awns; measurements of the spikelets, glumes, and lemmas do not. No attempt has been made to develop distribution maps.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
"decumbent" is not a number.