Carex texensis
Mem. Torrey Bot. Club 5: 97. 1894.
Plants without conspicuous rhizomes. Culms 10–30 cm, 0.5–1 mm wide basally, 0.4–0.5 mm wide distally. Leaves: sheaths tight, green, fronts hyaline; ligules less than 2 mm, wider than long; widest leaf-blades 1–1.7 mm wide. Inflorescences with 3–8 spikes, 0.6–3 cm × 5–6 mm; proximal internodes 1–2 times as long as proximal spikes; proximal bracts to 1 (–3) cm; spikes with 3–10 spreading or reflexed perigynia. Pistillate scales hyaline or pale-brown with green midvein, ovate, 1.8–2.4 × 0.8–1.3 mm, body 2/3 to almost length of perigynia, apex acute, acuminate or short-awned. Anthers 1 mm. Perigynia green to pale-yellow, faces not veined, 2.6–3.4 × 1–1.3 mm, base of body spongy, thickened, longitudinally striate adaxially, spongy region 0.7–1.1 mm, margins entire, usually serrulate distally; beak 0.7–1.1 mm, apical teeth 0.1–0.3 mm. Stigmas straight or slightly twisted, 0.05 mm wide. Achenes ovate, 1.3–1.5 × 1–1.1 mm.
Phenology: Fruiting spring.
Habitat: Dry to wet-mesic open forests and fields, often rocky or sandy substrates
Elevation: 50–300 m
Distribution
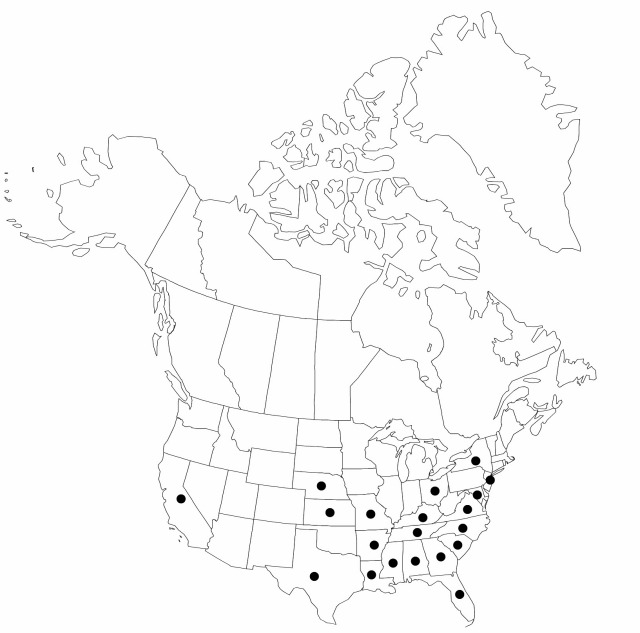
Ala., Ark., Calif., Fla., Ga., Kans., Ky., La., Md., Miss., Mo., Nebr., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, S.C., Tenn., Tex., Va.
Discussion
Carex texensis is introduced into California, New Jersey, New York and Ohio. Due to confusion with C. retroflexa, C. texensis is probably under-recorded.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"shortened" is not a number."widest" is not a number.