Eriogonum aliquantum
Phytologia 34: 460. 1976.
Herbs, erect to spreading, annual, 1.5–3.5 dm, sparsely villous, grayish. Stems: caudex absent; aerial flowering-stems erect, solid, not fistulose, 0.3–0.7 dm, sparsely villous. Leaves basal and cauline; basal: petiole 1.5–2.5 cm, sparsely villous, blade elliptic to broadly elliptic, 1.5–2 × 1–1.5 cm, glabrous and green on both surfaces, margins entire, villous; cauline: petiole 0.5–1 cm, sparsely villous, blade elliptic, 0.5–1.5 × 0.2–1 cm, similar to basal blade. Inflorescences cymose, open, 15–25 × 15–25 cm; branches not fistulose, sparsely villous; bracts 3, scalelike, 1–4 × 1–3 mm. Peduncles absent or rarely 1 at proximal node, erect, straight, slender, 0.3–0.7 cm, villous. Involucres turbinate-campanulate, 1–1.3 × 1–1.2 mm; teeth 5, erect, 0.4–0.6 mm. Flowers 1.2–2 mm, glabrous; perianth yellowish with darker yellowish-brown to reddish-brown midribs, glabrous; tepals monomorphic, oblanceolate; stamens exserted, 1.3–1.5 mm; filaments glabrous. Achenes shiny light-brown to brown, 3-gonous, 1.7–2.3 mm, glabrous.
Phenology: Flowering Jun–Aug.
Habitat: Clayey flats, saltbush and sagebrush communities, montane conifer woodlands
Elevation: 1900-2100 m
Discussion
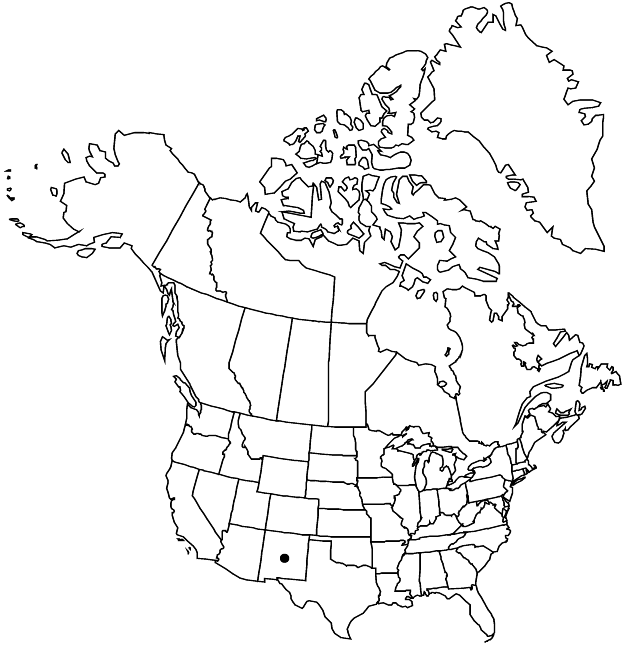
Eriogonum aliquantum is known only from the Cimarron, Vermejo, and Canadian river basins in Colfax County. Morphologically it is similar to E. visheri from the northern Great Plains, and a clear distinction is not always possible. Although considered a candidate for federal protection since the late 1970s, E. aliquantum remains essentially forgotten.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
"dm" is not declared as a valid unit of measurement for this property.