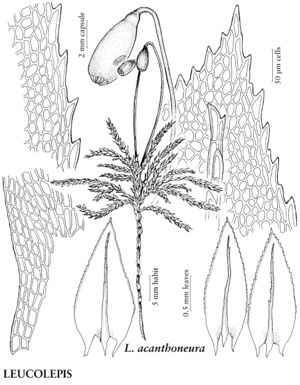
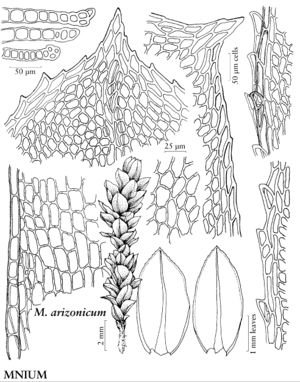
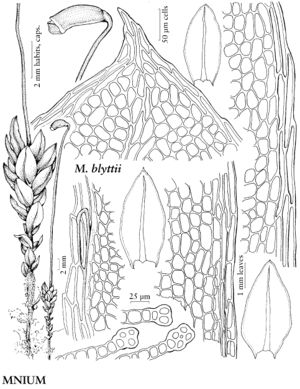
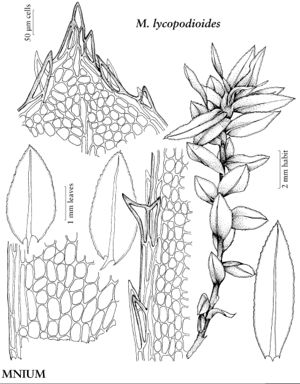
Mniaceae
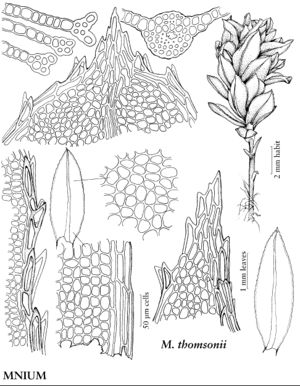
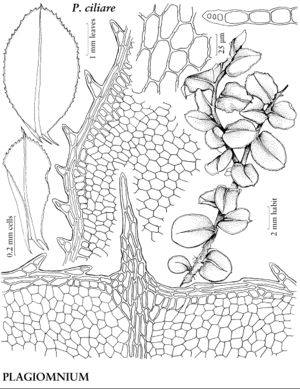
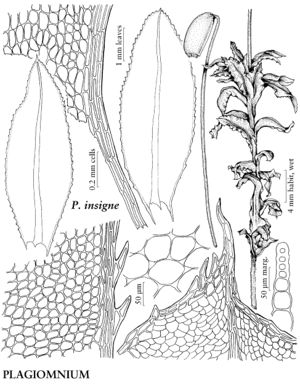
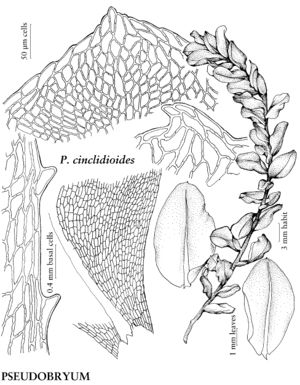
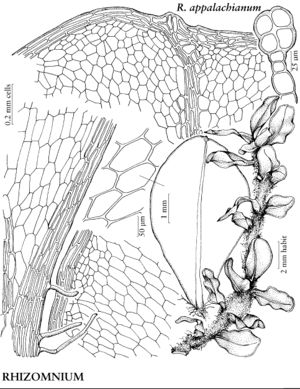
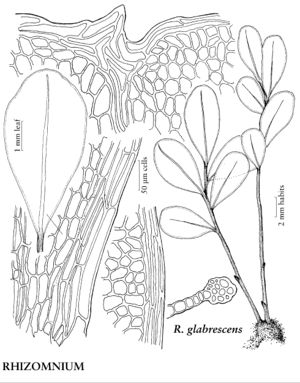
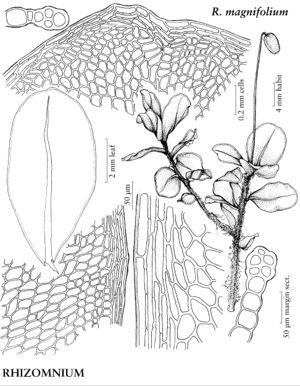
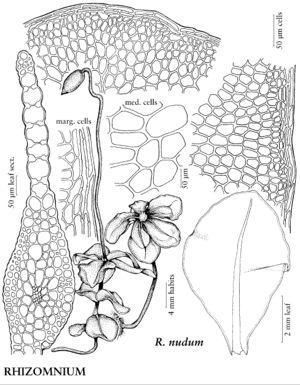
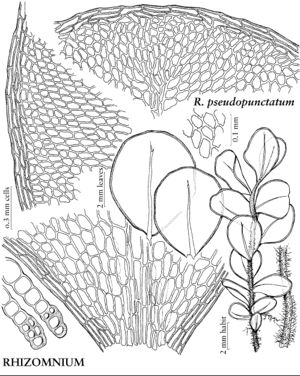
Plants small to large, in loose to dense tufts or mats. Stems green, yellow-green, brown, reddish-brown, or black, rarely yellowish-brown, erect, arching, inclined, or plagiotropic, usually simple, sometimes branched distally, rarely dendroid; rhizoids brown or reddish-brown, of two types, macronemata larger and usually strongly branched, mainly proximal, often matted, mainly restricted to leaf or branch bases distally, rarely along leaf-bases, and micronemata, smaller, less branched and paler, present or absent on stems. Leaves green, yellowish green, or reddish, rarely bluish green, usually small and distant proximally, larger and more crowded distally, sometimes forming terminal rosettes, sometimes incurved upwards, usually crisped or contorted, sometimes undulate when dry, spreading, erect-spreading, reflexed, or arcuate-recurved, flat or sometimes keeled, rarely undulate when moist, orbicular, spatulate, lingulate, ligulate, elliptic, ovate, ovatelanceolate, or obovate; base decurrent or not; margins usually plane, sometimes recurved, green, brown, red, or reddish-brown, 1-stratose or 2-stratose, rarely multistratose, rarely with stereid band, entire or toothed distally or to leaf base, teeth single or paired, sharp or blunt, of 1 (–4) cells; apex acute, obtuse, acuminate, or rounded, sometimes emarginate or retuse, often apiculate, sometimes cuspidate, cusp often toothed; costa single, excurrent, percurrent, subpercurrent, or ending well before apex, distal abaxial surface smooth or toothed, adaxial surface rarely toothed, teeth of 1 (–3) cells, 1 or 2 stereid bands present, rarely absent, (abaxial stereid band U-shaped in Cinclidium); alar cells undifferentiated; medial laminal cells usually short-elongate, sometimes ± isodiametric, hexagonal, sometimes pentagonal, rarely four-sided, usually 2: 1 or less (3+:1 in Pseudobryum), sometimes in longitudinal or diagonal rows, smooth (mammillose in Trachycystis), collenchymatous or not, walls pitted or not; marginal cells usually differentiated, linear, rhomboidal, or rectangular, in (1–) 2–3 (–6) rows. Sexual condition synoicous or dioicous. Seta single or sometimes double or several, yellow, brown, red, yellowish green, yellowish-brown, reddish-brown, or orange-yellow, sometimes blackish with age, elongate, straight or flexuose, smooth. Capsule horizontal to pendent, yellow, brown, yellowish-brown, or yellowish green, elliptic, ovate, subglobose, oblong, or cylindric; stomata cryptoporous (phaneroporous in Cyrtomnium); annulus deciduous; operculum conic or hemispheric, apiculate, mammillate, or rostrate; peristome double, complete; exostome teeth 16, usually lanceolate-acuminate, external surface lamellose; endostome usually equal in size to exostome, basal membrane high, segments often perforate with gaps along keels, cilia nodulose (endostome domed, fused at apex, perforated when mature, with keeled columns distally, alternating with shorter exostome teeth in Cinclidium). Calyptra cucullate, usually naked. Spores spheric, smooth or papillose, brown.
Distribution
Nearly worldwide, circumtemperate to circumboreal
Discussion
Genera 12, species 92 (8 genera, 37 species in the flora).
Mniaceae is a diverse family generally characterized by relatively large plants with broad leaves, and with short-elongate or more or less isodiametric laminal cells most often hexagonal and angular. Leaf margins are usually differentiated by a border of elongate cells and range from smooth to strongly toothed. The family is also characterized by a wide degree of morphological variation as a response to environmental conditions, age, or sexuality. Fertile stems are sometimes strikingly different from sterile stems, and female or synoicous plants are sometimes different from male plants. This makes the identification of weakly developed specimens difficult. Many species in the family are fairly common in temperate and boreal habitats in the Northern Hemisphere and are frequently collected in ecologically based surveys.
The following keys stress vegetative traits and are best employed using well-developed, mature plants. Leaf laminal and marginal cell characters were derived by examining cells near mid leaf.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
Illustrations
Key
| 1 | Stems dendroid | > 2 |
| 1 | Stems not dendroid | > 3 |
| 2 | Branch leaves ovate-lanceolate. | Leucolepis |
| 2 | Branch leaves ligulate or lingulate. | Plagiomnium |
| 3 | Medial laminal cells mammillose; specialized asexual reproduction by flagelliform branches; Alaska. | Trachycystis |
| 3 | Medial laminal cells smooth; specialized asexual reproduction absent or present, not by flagelliform branches; widespread | > 4 |
| 4 | Leaf marginal teeth paired. | Mnium |
| 4 | Leaf marginal teeth single or teeth absent | > 5 |
| 5 | Medial laminal cells usually 3+:1; marginal cells indistinctly differentiated. | Pseudobryum |
| 5 | Medial laminal cells 2:1 or less, rarely longer; marginal cells usually strongly differentiated | > 6 |
| 6 | Plagiotropic or arching sterile stems usually present (absent in P. venustum); leaf margins toothed, teeth often well developed and sharp, sometimes nearly absent and blunt; stems lacking red pigmentation. | Plagiomnium |
| 6 | Plagiotropic or arching sterile stems usually absent, occasionally present; leaf margins entire or toothed, teeth weakly developed when present, usually blunt; stems sometimes reddish | > 7 |
| 7 | At least some leaf margins toothed, teeth usually reduced, often appearing as small extensions of distal cell ends. | Mnium |
| 7 | Leaf margins entire | > 8 |
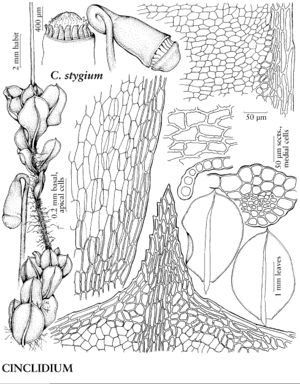
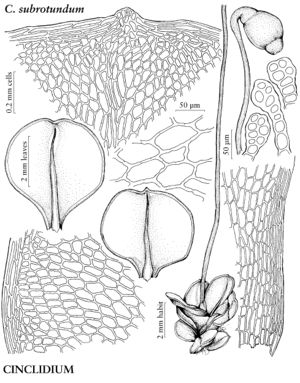
| 8 | Macronemata in longitudinal rows, micronemata absent; costal abaxial stereid band U-shaped; endostome segments fused into dome. | Cinclidium |
| 8 | Macronemata not in longitudinal rows, micronemata present or absent; costal abaxial stereid band not U-shaped; endostome segments free | > 9 |
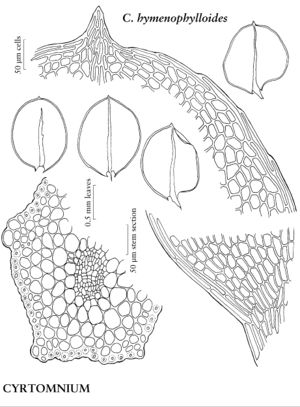
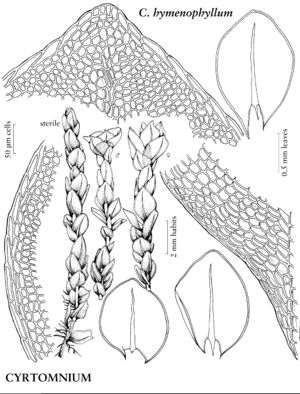
| 9 | Mature stems brown or black, lacking red pigmentation; leaves ovate or broadly elliptic; margins 1-stratose; stomata phaneroporous. | Cyrtomnium |
| 9 | Mature stems often red or reddish brown; leaves obovate, elliptic, or rarely ± orbicular; margins 1-4-stratose; stomata cryptoporous. | Rhizomnium |