Dichanthelium
Plants perennial; cespitose, sometimes rhizomatous, sometimes with hard, cormlike bases, often with basal winter rosettes of leaves having shortly ovate to lanceolate blades, these often sharply distinct from the blades of the cauline leaves. Culms 5-150 cm, herbaceous, hollow, usually erect or ascending, rarely sprawling, in the spring often spreading, sometimes decumbent in the fall, usually branching from the mid or lower culm nodes in summer and fall; branches rebranching 1-4 times, terminating in small secondary panicles that usually partly included in the sheaths. Cauline leaves 3-14, usually distinctly longer and narrower than the rosette blades; ligules of hairs, membranous, or membranous and ciliate, sometimes absent; pseudoligules of 1-5 mm hairs often present at the bases of the blades immediately behind the true ligules; blades usually distinctly longer and narrower than those of the basal rosette, cross-sections with non-kranz anatomy; photosynthesis C3. Inflorescences panicles, terminal on the culms and branches; sterile branches and bristles absent; disarticulation below the glumes. Primary panicles terminating the culms, developing April-june (July), sometimes also in late fall, usually at least partially chasmogamous, often with a lower seed set than the secondary pani¬cles; secondary panicles terminating the branches, produced from (May) June to fall, usually partially or totally cleistogamous. Spikelets 0.8-5.2 mm, not subtended by bristles, dorsally compressed, surfaces unequally convex, apices unawned. Glume apices not or only slightly gaping at maturity; lower glumes 1/5 – 3/4 as long as the spikelets, 1-5-veined, truncate, acute, or acuminate; upper glumes slightly shorter than the spikelets or exceeding the upper florets by up to 1 mm, 5-11-veined, not saccate, apices rounded to attenuate. Lower florets sterile or staminate; lower lemmas similar to the upper glumes; lower paleas sometimes present, thin, shorter than the lower lemmas; upper florets bisexual, sessile, plump, usually apiculate to mucronate, sometimes minutely so, or subacute to (rarely) acute; upper lemmas striate, chartaceous-indurate, shiny, usually glabrous, margins involute; upper paleas striate; lodicules 2; anthers 3. Caryopses smooth; pericarp thin; endosperm hard; hila round or oval, x = 9.
Distribution
Minn., Conn., N.J., N.Y., Wash., Ala., Mich., N.C., Pa., Puerto Rico, S.C., W.Va., Ark., Iowa, Kans., Mo., N.Dak., Nebr., Okla., S.Dak., Del., D.C, Wis., Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr. (Labr.), N.S., Ont., P.E.I., Que., Sask., Pacific Islands (Hawaii), Md., Mass., Maine, N.H., R.I., Vt., Fla., Wyo., Miss., Ariz., N.Mex., Tex., La., Ga., Tenn., Calif., Nev., Colo., Ill., Ind., Va., Idaho, Ohio, Utah, Mont., Oreg., Ky.
Discussion
Dichanthelium is a genus of approximately 72 species, 34 of which are native to the Flora region. It is often included in Fanicum, the two taxa being similar in gross morphology. Recent molecular data reinforce the morphological arguments for recognizing Dichanthelium as a distinct genus.
When the branches of Dichanthelium develop, in late summer or fall, the culms acquire a very different aspect; comments about the 'fall phase' refer to the appearance of the plant or its culms following this branching. Unless stated otherwise, descriptions and measurements refer to structures of the culms and primary panicles, not those of the branches and secondary pani¬cles. Ligule measurements usually include the hairs of the pseudoligule, if present, because the two are often difficult to distinguish with less than 30x magnification.
Selected References
Lower Taxa
Key
| 1 | Basal leaf blades similar in shape to those of the lower cauline leaves, usually erect to ascending, clustered at the base, sometimes small or vestigial; culms branching from near the base in the fall, with 2-4 leaves, only the upper 2-4 internodes elongated. | > 2 |
| 2 | Blades soft, 3-12 mm wide, usually ciliate; upper blades less than 20 times as long as wide; fall phase with short panicle-bearing branches, without sterile shoots (sect. Strigosa). | > 3 |
| 3 | Leaf sheaths with retrorse or spreading hairs; upper blades 4-17 cm long, at least 3/4 as long as the basal blades; blade margins usually finely short ciliate, the cilia not papillose-based; spikelets with papillose-based hairs | Dichanthelium laxiflorum |
| 3 | Leaf sheaths glabrous or with ascending hairs; upper blades 1.5-6 cm long, less than 3/4 as long as the basal blades; blade margins with papillose-based cilia; spikelets glabrous or pubescent, hairs not papillose-based | Dichanthelium strigosum |
| 2 | Blades stiff, 1-5 mm wide, not ciliate; most upper blades at least 20 times as long as wide; fall phase with basal panicles and sterile shoots (sect. Linearifolia). | > 3 |
| 4 | Upper glumes and lower lemmas forming a beak extending 0.2-1 mm beyond the upper florets; spikelets 3.2-4.3 mm long; primary panicles with 7-25 spikelets | Dichanthelium depauperatum |
| 4 | Upper glumes and lower lemmas equaling or exceeding the upper florets by no more than 0.3 mm, not forming a beak; spikelets 2-3.4 mm long; primary panicles with 12-70 spikelets. | > 5 |
| 5 | Cauline blades 4-8 cm long, all alike; basal blades ascending to spreading | Dichanthelium wilcoxianum |
| 5 | Uppermost cauline blades 10-20 cm long, distinctly longer than the lower blades; basal blades erect to ascending. | > 6 |
| 6 | Panicles 1-3 cm wide, with ascending branches and appressed pedicels; spikelets turgid, 2.6-3.4 mm long, 1-1.7 mm wide, upper florets obovoid | Dichanthelium perlongum |
| 6 | Panicles 2-6 cm wide, with spreading branches and pedicels; spikelets not turgid, 2-3.2 mm long, 0 8-1.4 mm wide, upper florets ellipsoid | Dichanthelium linearifolium |
| 1 | Basal leaf blades usually well-differentiated from the cauline blades, ovate to lanceolate, spreading, forming a rosette, or basal blades absent; culms usually branching from the midculm nodes in the fall, with 3-14 leaves, usually all internodes elongated. | > 2 |
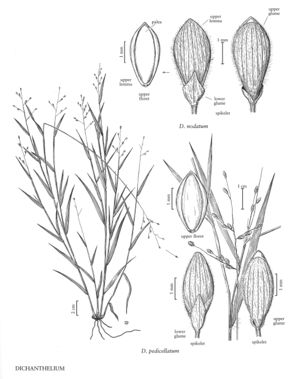
| 7 | Bases of the culms hard, cormlike; basal rosettes absent; spikelets with papillose-based hairs and attenuate basally (sect. Pedicellata). | > 8 |
| 8 | Culms erect in the spring; cauline leaves 4-7, with thin, glabrous or sparsely hirsute blades that widen distal to the rounded to subcordate bases; lower glumes not encircling the pedicels, subadjacent to the upper glumes | Dichanthelium pedicellatum |
| 8 | Culms decumbent to ascending in the spring; cauline leaves 8-14, with thick, firm, puberulent blades that are parallel-sided distal to the rounded to truncate bases; lower glumes almost to completely encircling the pedicels, attached about 0.2 mm below the upper glumes | Dichanthelium nodatum |
| 7 | Bases of the culms not cormlike; basal rosettes usually present; spikelets not both with papillose-based hairs and attenuate basally. | > 8 |
| 9 | Blades cordate, thick, with white, cartilaginous margins; spikelets usually spherical to broadly obovoid or broadly ellipsoid, 1-1.8 mm long (sect. Sphaerocarpa). | > 10 |
| 10 | Spikelets 1-1.4 mm long; lower glumes 0.2-0.4 mm long; cauline blades 5-10 mm wide | Dichanthelium erectifolium |
| 10 | Spikelets 1.3-1.8 mm long; lower glumes 0.4-0.8 mm long; cauline blades 5-25 mm wide. 11. Cauline blades 4-7,10-25 cm long, 14-25 mm wide, with evident veins; culms nearly erect; panicles less than 1/2 as wide as long | Dichanthelium polyanthes |
| 11 | Cauline blades 3-4(6), 1.5-10 cm long, 5-14 mm wide, with obscure veins; culms decumbent or ascending; panicles more than 1/2 as wide as long | Dichanthelium sphaerocarpon |
| 9 | Blades not cordate or the spikelets not both spherical and less than 1.9 mm long; blade margins usually not white and cartilaginous. | > 10 |
| 12 | Lower glumes thinner and more weakly veined than the upper glumes, attached about 0.2 mm below the upper glumes, the bases clasping the pedicels; spikelets attenuate basally. | > 13 |
| 13 | Blades 2-7 cm long, about 10 times as long as wide, not or slightly involute, spreading, without raised veins, not longitudinally wrinkled; spikelets obovoid-obpyriform, planoconvex in side view (sect. Lancearia) | Dichanthelium portoricense |
| 13 | Blades 4-16 cm long, more than 14 times as long as wide, or involute, stiffly erect or ascending, with prominently raised veins, the lower blades usually longitudinally wrinkled; spikelets ellipsoid to obovoid, biconvex in side view (sect. Angustifolia). | > 14 |
| 14 | Culms densely villous; nodes densely bearded; spikelets densely pubescent | Dichanthelium consanguineum |
| 14 | Culms glabrous, puberulent, or pilose with papillose-based hairs; nodes glabrous, puberulent to lightly bearded; spikelets glabrous or pubescent | Dichanthelium aciculare |
| 12 | Lower glumes similar in texture and vein prominence to the upper glumes, attached immediately below the upper glumes, the bases not clasping the pedicels; spikelets usually not attenuate basally. | > 13 |
| 15 | Culms arising from rhizomes 3-5 mm thick, with (5)7-14 cauline blades; sheaths strongly hispid or viscid, mottled with pale spots, constricted at the top (sect. Clandestina). | > 16 |
| 16 | Nodes densely bearded above a viscid glabrous ring, often swollen; blades densely soft pubescent | Dichanthelium scoparium |
| 16 | Nodes glabrous or sparsely pubescent, not swollen; blades glabrous or sparsely pubescent. | > 17 |
| 17 | Cauline blades 7-15 mm wide, apices involute, long tapering; spikelets glabrous or sparsely puberulent | Dichanthelium scabriusculum |
| 17 | Cauline blades 15-30 mm wide, apices flat, acuminate; spikelets sparsely pubescent | Dichanthelium clandestinum |
| 15 | Culms arising from caudices or from rhizomes to 2 mm thick, with 3-7(9) cauline blades; sheaths not viscid, rarely hispid, not mottled with pale spots or constricted at the top. | > 16 |
| 18 | Ligules with a membranous base, ciliate distally; culms usually arising from slender rhizomes; lower florets often staminate; cauline blades 5-40 mm wide, often with a cordate base (sect. Macrocarpa). | > 19 |
| 19 | Spikelets ellipsoid, not turgid, with pointed apices; cauline blades 4-6, cordate at the base; sheaths without papillose-based hairs. | > 20 |
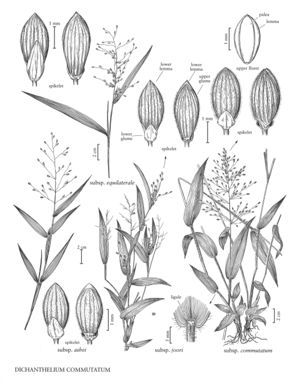
| 20 | Spikelets 2.2-3.2 mm long; ligules about 0.3 mm long; blades 5-25 mm wide; lower floret sterile | Dichanthelium commutatum |
| 20 | Spikelets 2.9-5.2 mm long; ligules 0.4-0.9 mm long; blades 15-40 mm wide; at least some lower florets staminate. | > 21 |
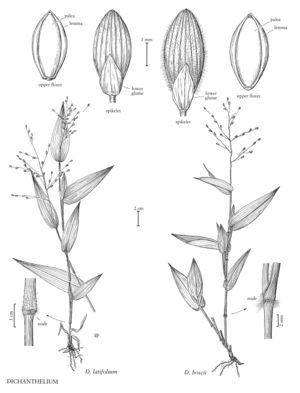
| 21 | Nodes glabrous or slightly bearded; spikelets 2.9-3.9 mm long | Dichanthelium latifolium |
| 21 | Nodes densely retrorsely bearded; spikelets 3.8-5.2 mm long | Dichanthelium boscii |
| 19 | Spikelets obovoid, turgid, with rounded apices; cauline blades 3-4, tapered, rounded or truncate to cordate at the base; sheaths with papillose-based hairs. 22. Blades and spikelets with papillose-based hairs; panicles usually slightly longer than wide, with spreading to ascending branches | Dichanthelium leibergii |
| 22 | Blades glabrous; spikelets puberulent to almost glabrous; panicles usually more than twice as long as wide, with nearly erect branches | Dichanthelium xanthophysum |
| 18 | Ligules of hairs (except for D. nudicaule); culms arising from caudices; lower florets sterile; cauline blades 1-18 mm wide, bases usually tapered, rounded, or truncate at the base, sometimes cordate. | > 19 |
| 23 | Lower internodes short, upper nodes elongated; flag leaves distant and much reduced; culms rarely branching in the fall; branches, if present, few, developing from basal and subbasal nodes, erect (sect. Nudicaulia) | Dichanthelium nudicaule |
| 23 | Lower internodes about as long as the upper internodes; flag leaves usually not much reduced; culms branching in the fall; branches often many, developing from mid- or upper culm nodes, often spreading. | > 24 |
| 24 | Spikelets 2.5-4.3 mm long, usually obovoid, turgid; upper glumes usually with an orange or purple spot at the base, the veins prominent (sect. Oligosantha). | > 25 |
| 25 | Nodes glabrous or sparsely pubescent; abaxial surfaces of the blades glabrous or pubescent, but not velvety pubescent | Dichanthelium oligosanthes |
| 25 | Nodes bearded with spreading to retrorse hairs; abaxial surfaces of the blades softly velvety pubescent. | > 26 |
| 26 | Spikelets 3.7-4.3 mm long; culms 2-3 mm thick, stiffly erect; ligules 2-5 mm long, without pseudoligules; blades glabrous or sparsely pilose on the adaxial surfaces | Dichanthelium ravenelii |
| 26 | Spikelets 2.5-3.2 mm long; culms usually 1-2 mm thick, erect; ligules 0.5-1 mm long, with the adjacent pseudoligules 1-3 mm long; blades densely velvety pubescent on both surfaces | Dichanthelium malacophyllum |
| 24 | Spikelets 0.8-3 mm long, ellipsoid or obovoid, not turgid; upper glumes lacking an orange or purple spot at the base and the veins not prominent. | > 25 |
| 27 | Ligules and adjacent pseudoligules 1-5 mm long, or the culms and sheaths with long hairs and also puberulent; spikelets variously pubescent to subglabrous (sect. Lanuginosa). | > 28 |
| 28 | Spikelets 0.8-1.1 mm long, puberulent to subglabrous; culms delicate, 0.3-0.8 mm thick | Dichanthelium wrigbtianum |
| 28 | Spikelets 1.1-3 mm long, variously pubescent; culms not delicate, usually more than 1 mm thick. | > 29 |
| 29 | Spikelets 1.1-2.1 mm long; sheaths glabrous or pubescent with hairs no more than 3 mm long | Dichanthelium acuminatum |
| 29 | Spikelets 1.8-3 mm long; sheaths with hairs to 4 mm long | Dichanthelium ovale |
| 27 | Ligules absent or to 1.8 mm long, without adjacent pseudoligules; culms and at least the upper sheaths glabrous or sparsely pubescent with hairs of 1 length only; spikelets glabrous or pubescent. | > 28 |
| 30 | Culms (18)40-100 cm tall, rarely delicate, usually more than 1 mm thick; spikelets 1.5-2.7 mm long; blades 3.5-14 cm long, 5-14 mm wide (sect. Dichanthelium.). | > 31 |
| 31 | Spikelets glabrous or, if pubescent, either the nodes bearded or the culms weak and prostrate; blade of the flag leaf usually spreading | Dichanthelium dichotomum |
| 31 | Spikelets pubescent; nodes glabrous; culms erect or ascending; blade of the flag leaf erect or ascending | Dichanthelium boreale |
| 30 | Culms 5-40(55) cm tall, delicate, usually less than 1 mm thick; spikelets 1.1-1.7 mm long; longest blades 1.5-6 cm long, 1.5-6 mm wide (sect. Ensifolia). | > 31 |
| 32 | Culms reclining or weakly erect; cauline blades 4-9, usually without prominent white, cartilaginous margins; ligules often more than 1 mm long | Dichanthelium ensifolium |
| 32 | Culms erect, sometimes geniculate basally; cauline blades 3-5, with prominent white, cartilaginous margins; ligules 0.2-0.7 mm long. | > 33 |
| 33 | Culms few per clump; the fall phase branching sparingly; cauline blades flat, the bases rounded; blades of the flag leaves much shorter than those of the lower leaves | Dichanthelium tenue |
| 33 | Culms many per clump; the fall phase branching extensively; cauline blades often involute, the bases subcordate; blades of the flag leaves only slightly shorter than those of the lower leaves | Dichanthelium chamaelonche |
"usually distinctly longer and narrower" is not a number."decumbent" is not a number.